




The rise of artificial intelligence has created a new breed of data center—one that demands unprecedented levels of power, cooling, and most critically, network performance. Unlike traditional data centers that handle everyday computing tasks, AI data centers are purpose-built facilities for training and running large-scale machine learning models.
Understanding what makes these facilities unique helps explain why network infrastructure has become the make-or-break factor in AI success.
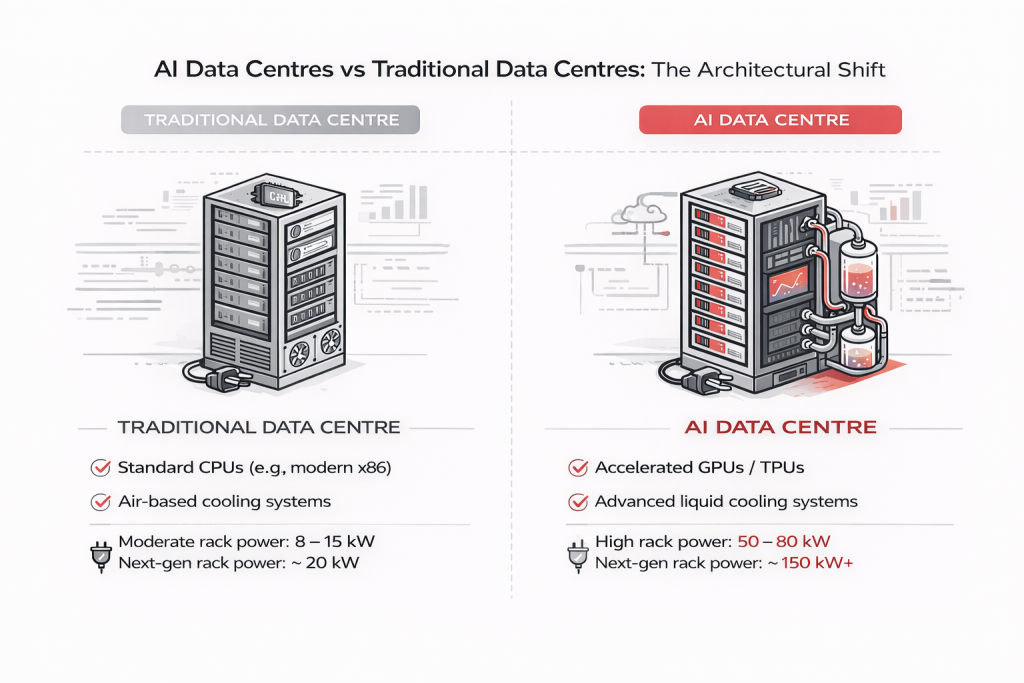
Traditional data centers are generalists. They run business applications, host websites, store databases, and handle email servers. Each task operates independently with moderate resource demands.
AI data centers are specialists built for one primary function: training and running neural networks at massive scale. This singular focus reshapes everything from processor choice to building design.
The fundamental shift starts with processors.
Traditional data centers rely on CPUs designed to handle diverse, sequential tasks efficiently—perfect for running varied business applications.
AI data centers are built around GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and specialized AI accelerators like TPUs. These chips contain thousands of simple cores working in parallel, ideal for the repetitive mathematical operations required in machine learning.
Training an AI model requires massive parallel processing. Where a CPU handles tasks sequentially, a GPU operates like thousands of workers performing identical operations simultaneously.
Here’s where AI data centers diverge completely from traditional thinking.
Servers communicate occasionally. Standard Ethernet handles sporadic, low-volume traffic between independent systems.
Thousands of GPUs must operate as a single unified system. When training large models, processors constantly synchronize their work, exchanging terabytes of data with near-zero latency tolerance.
Even milliseconds of delay cascade into hours of wasted training time. This demands:
Without proper network infrastructure, multi-million dollar GPU clusters operate at a fraction of their potential.
AI computation generates extreme heat. Standard server racks draw 5-10 kilowatts. AI-optimized racks consume 50-100 kilowatts—equivalent to powering 20 homes from a single cabinet.
Air cooling cannot handle this density. Modern AI facilities use:
This physical complexity demands careful planning and monitoring to maintain optimal performance.
AI training consumes massive datasets—petabytes of images, text, and video. Unlike traditional databases, AI storage operates like a high-speed conveyor belt delivering continuous data streams to thousands of GPU workers.
Success requires:
The bottleneck isn’t finding data—it’s moving it fast enough to keep GPUs fully utilized.
AI data centers aren’t retrofitted warehouses. They’re industrial facilities designed from the ground up:
Managing AI data center networks presents unique challenges:
Scale: Thousands of 400G/800G fiber connections between GPU clusters, storage, and control systems.
Interdependence: Systems are tightly coupled. Network degradation directly impacts GPU utilization and training efficiency.
Performance Sensitivity: AI workloads expose network issues that traditional applications tolerate.
Rapid Evolution: Infrastructure changes constantly as new GPU generations and networking technologies emerge.
Organizations need robust network infrastructure capable of supporting these demanding workloads while maintaining visibility and control.
Current AI models are limited by available infrastructure. Future demands will intensify:
With higher network bandwidth requirements triggered by AI, bandwidth consumption for broadband is set to surge higher. With higher bandwidth requirements, ISPs and telcos need to handle increased loads on their BSS and Logging solutions. Jaze ISP Manager provides a scalable architecture to adopt to increased loads on their infrastructure without incurring significant hardware investment. Click here to discover how Jaze ISP Manager supports a scalable architecture for large scale ISP networks. Click here to learn more.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are among the most disruptive cyber threats faced by organizations today. Unlike attacks that steal data quietly, DDoS attacks are loud, aggressive, and designed to bring digital services to a complete halt. As businesses become more dependent on online platforms, understanding DDoS attacks is no longer optional—it is essential for survival in the digital ecosystem.
This article explains what DDoS attacks are, how they operate, why they are dangerous, and how organizations can prepare for them.
A DDoS attack is an attempt to make an online service unavailable by overwhelming it with excessive traffic. Instead of a single source sending requests, a DDoS attack uses thousands or even millions of systems at the same time. These systems work together to flood the target with traffic until it can no longer respond to legitimate users.
The “distributed” nature of the attack makes it difficult to block, as the traffic appears to come from many different locations rather than a single attacker.
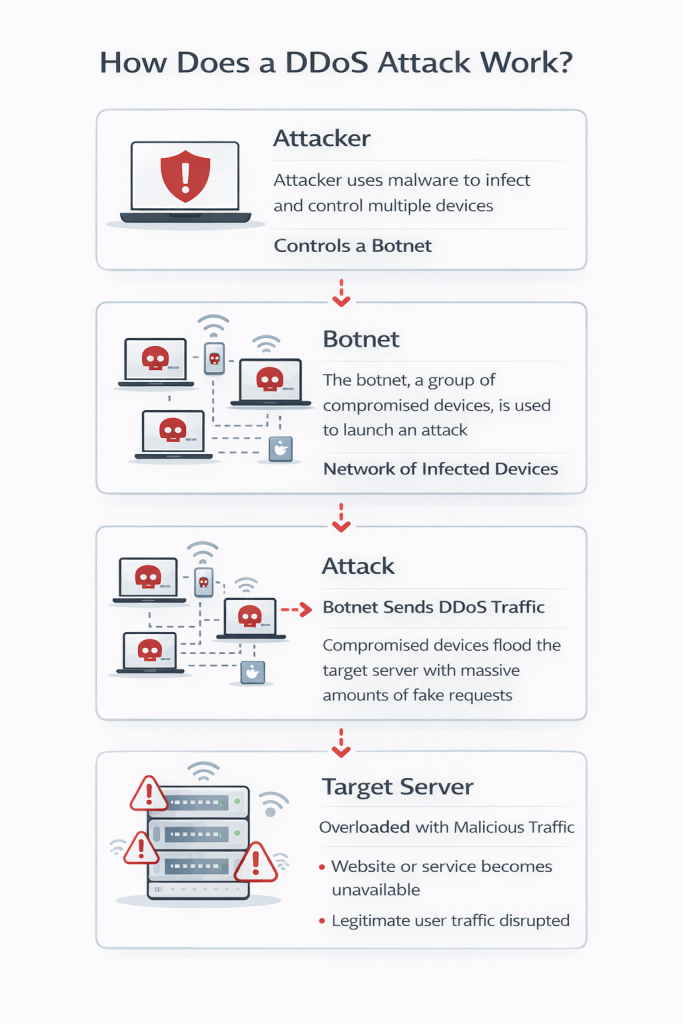
Most DDoS attacks rely on a network of compromised devices known as a botnet. These devices may include computers, servers, routers, or internet-connected devices that have been infected with malicious software.
The typical attack process includes:
Because each device sends a small amount of traffic, the attack can be hard to detect in its early stages.
DDoS attacks can take different forms depending on the attacker’s goal and the weakness being targeted.

These attacks aim to consume all available bandwidth by sending massive amounts of traffic. The target becomes unreachable simply because the network capacity is exhausted.
Protocol attacks exploit weaknesses in how network connections are established and maintained. By sending incomplete or malformed requests, attackers force servers to waste resources handling fake connections.
These attacks target specific applications such as websites or APIs. They mimic normal user behavior, making them difficult to detect, while slowly exhausting server resources.
In more advanced scenarios, attackers combine multiple techniques at once. This makes mitigation more complex and increases the likelihood of prolonged downtime.
DDoS attacks are not just technical issues—they have real business consequences.
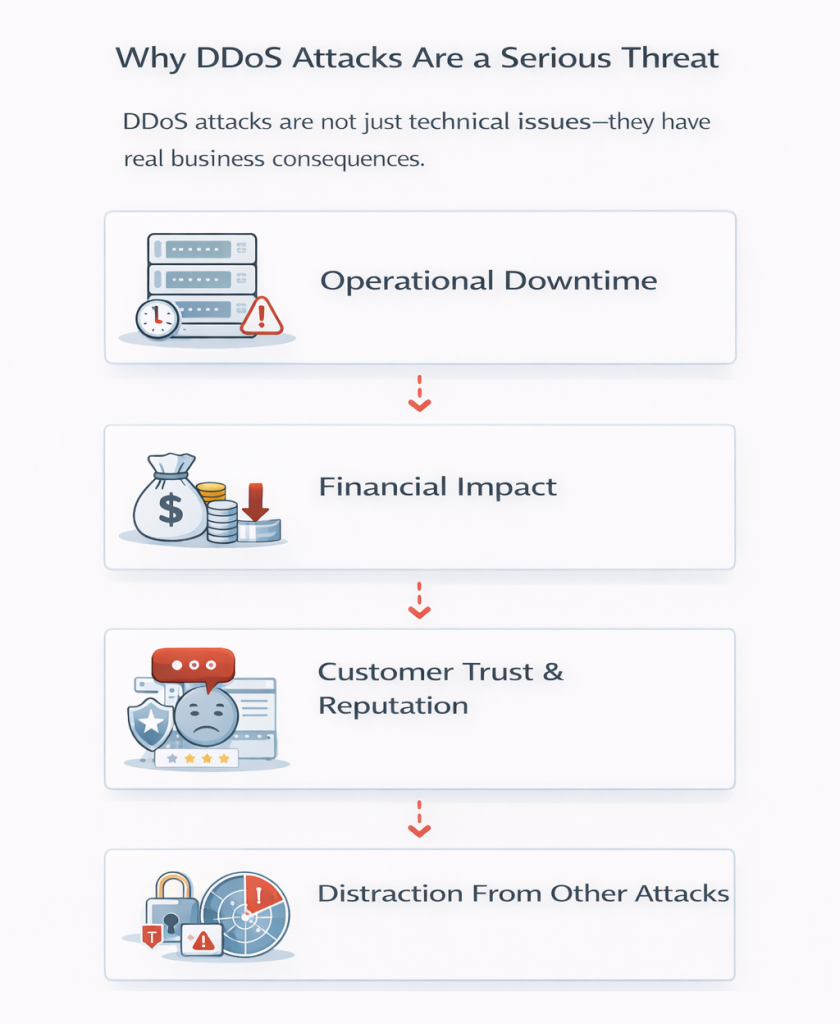
When services go offline, employees, customers, and partners are unable to access critical systems. Even a short outage can disrupt workflows and service delivery.
Lost revenue, recovery costs, and emergency mitigation efforts can quickly add up. For online-dependent businesses, downtime directly translates to financial loss.
Repeated service interruptions damage credibility. Users expect reliability, and prolonged outages can push customers toward competitors.
In some cases, DDoS attacks are used as a diversion while attackers attempt data breaches or system infiltration elsewhere.
Modern DDoS attacks are larger, faster, and more sophisticated than ever before. Attackers increasingly use automated tools and poorly secured internet-connected devices to amplify their attacks. Even small organizations are now being targeted, not just large enterprises.
The rise of cloud services and high-speed networks means attackers can generate enormous traffic volumes in seconds, leaving little time to react without proper defenses in place.
While it is impossible to eliminate the risk entirely, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure with the right approach.
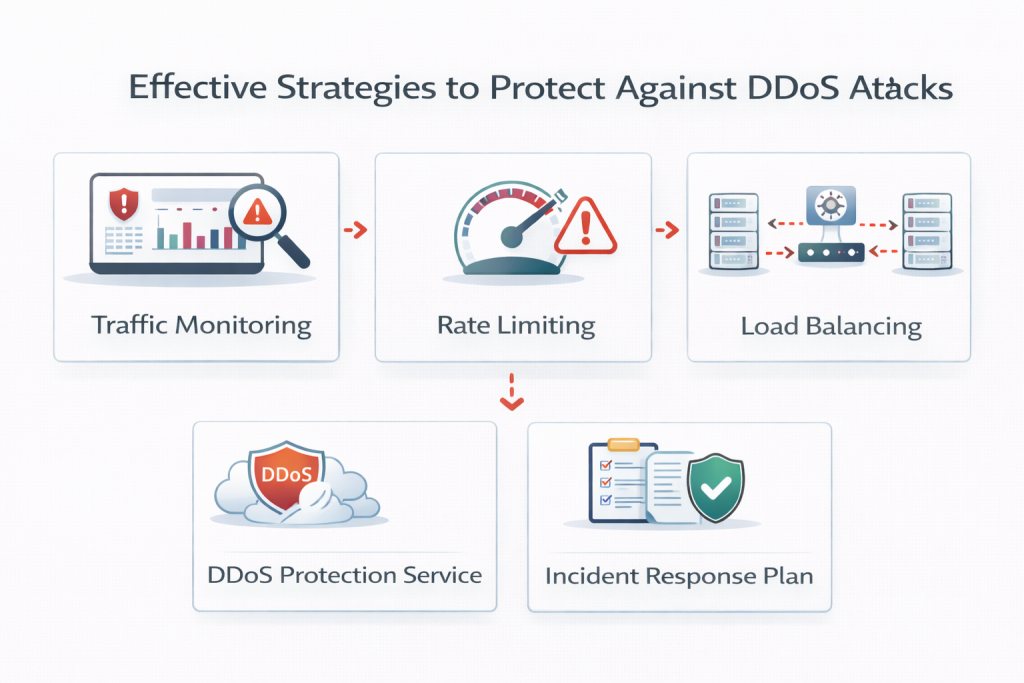
Monitoring normal traffic patterns helps identify sudden spikes or unusual behavior before systems fail.
Filtering malicious requests and limiting the number of requests per user reduces the impact of traffic floods.
Distributing workloads across multiple servers ensures that no single system becomes a point of failure.
Having predefined response procedures ensures faster recovery and minimizes confusion during an attack.
Regular testing, system updates, and security reviews also play a critical role in maintaining resilience.
DDoS attacks are designed to overwhelm, disrupt, and damage trust in digital services. As these attacks grow in scale and complexity, businesses must move beyond reactive responses and adopt proactive defense strategies.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs stay resilient against DDoS threats by offering deep network visibility and real-time traffic insights through IPFIX logging in real-time. Based on these logs ISPs can identify attacks and trigger RTBH or BGP Flowspec records to mitigate the attack. This proactive approach ensures uninterrupted service delivery and stronger network reliability.
On November 18, 2025, a major disruption rippled across the internet when Cloudflare—one of the world’s most widely used internet infrastructure providers—experienced a significant service outage. Because Cloudflare supports millions of websites with DNS, CDN caching, traffic filtering, API routing, and security layers, even a single malfunction can create global-level instability. And that’s exactly what millions of users witnessed that day: slow loading pages, apps refusing to open, authentication failures, and entire platforms temporarily unreachable.
While outages are not new in the digital world, this one stood out because of how deeply Cloudflare sits in the modern connectivity pipeline. In many ways, the incident offered a real-world reminder of how much of the internet relies on a few key infrastructure players.
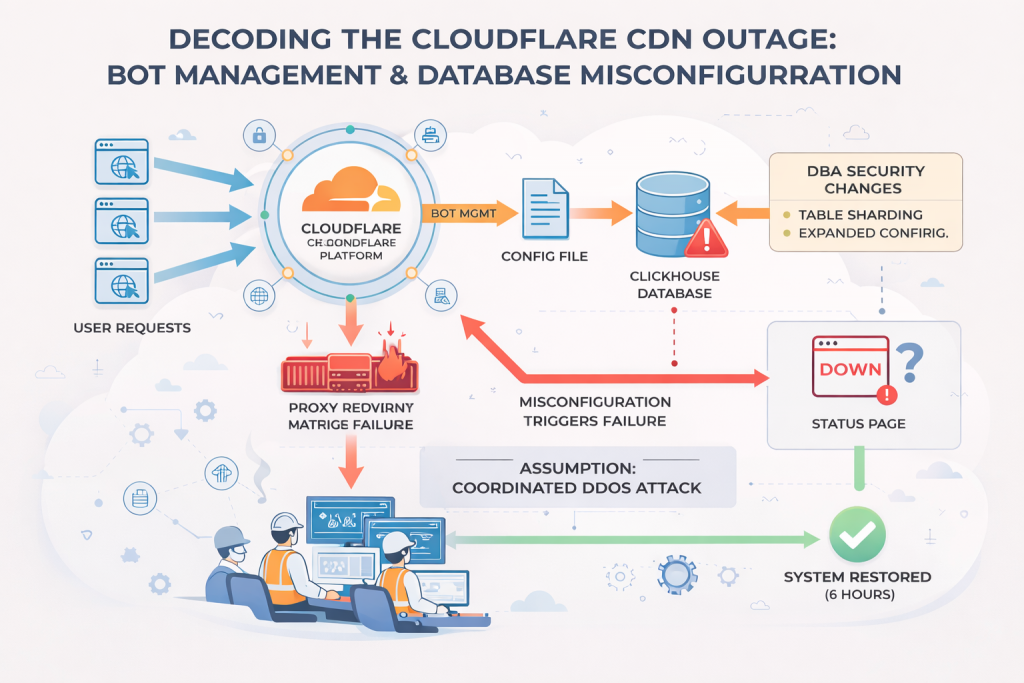
According to Cloudflare’s engineering investigation, the root cause was a faulty internal configuration deployed to part of their network. This configuration affected a critical service responsible for evaluating incoming requests and filtering harmful traffic. When the service encountered the corrupted configuration file, it failed in a “closed” state—meaning instead of allowing traffic through when uncertain, it blocked it.
This resulted in a surge of HTTP 5XX errors, especially 500 and 503 responses, which are typical indicators of server-side failures. Users around the world soon realized that websites using Cloudflare were timing out, stalling, or redirecting to error pages.
Unlike outages caused by connectivity failures or cyberattacks, this event was self-inflicted by a software deployment that didn’t behave as expected. Small configuration issues can have an outsized impact in distributed systems, and this incident highlighted how even a single misconfiguration in a shared global network can cascade quickly.
When Cloudflare pushed the problematic update, only part of the network received it at first. This meant some nodes were functioning normally while others were rejecting legitimate requests. As traffic routing systems attempted to balance loads across these nodes, users received unpredictable experiences—one moment a service worked, the next it failed.
This “flapping” behavior created instability until Cloudflare engineers isolated the issue, rolled back the configuration, and restored normal operations. Because Cloudflare’s infrastructure is interconnected, the rollback had to be done carefully to avoid further disruptions.
The outage lasted several hours for some regions, though others recovered sooner depending on local routing and DNS propagation.
The disruption was widely felt because Cloudflare isn’t simply a website host—it acts as a performance booster, security layer, and traffic gateway for businesses large and small. Popular platforms relying on Cloudflare for DNS or CDN saw sudden performance drops. E-commerce portals, SaaS dashboards, streaming services, and even mobile apps that depend on API calls struggled to function.
For many businesses, this meant:
Even organizations that had redundant hosting infrastructure were affected if they used Cloudflare for routing or DNS resolution.
Although Cloudflare increases performance and security for millions of websites, the outage showed how a single point of failure can disrupt a huge portion of online activity. Centralization offers efficiency but also creates vulnerability.
Many companies invest in multi-cloud or backup environments, but rely on a single provider for DNS or CDN. The outage highlighted why redundancy must cover every layer of the stack, including traffic routing and security services—not just compute resources.
Modern cloud platforms are highly automated, but that also means configuration errors can spread extremely fast. Even with safety checks, edge cases slip through. The best protection is layered testing, staged rollouts, and real-time anomaly detection.
Cloudflare acted quickly, pausing the rollout and identifying the failing component. Engineers issued a rollback, restarted affected services, and published a transparent incident update. Their communication emphasized that the issue was not caused by an attack, but by an internal logic failure during deployment.
The company also announced improvements to configuration validation, emphasizing stronger safeguards to prevent similar issues in the future.
The November 2025 outage is a valuable case study for businesses that rely heavily on cloud-based traffic tools:
Most importantly, organizations must acknowledge that outages are inevitable. The real question is how resilient the architecture remains when a critical provider becomes unavailable.
The Cloudflare outage of November 18, 2025 was a reminder of the complexity and fragility of the internet’s backbone. While Cloudflare resolved the issue efficiently and transparently, the event highlighted how interconnected digital services have become.
While ISPs cannot protect themselves from technical issues with the Internet, they can definitely adopt tools that strengthen operational visibility and fault management. Jaze ISP Manager provides powerful helpdesk and task management features to help teams detect and respond to internal outages faster.
The Internet today works much like a vast and rapidly expanding city. Every device — whether it’s your phone, laptop, or home router — needs a unique address to send and receive information. For decades, this addressing system depended on IPv4, a 32-bit structure that was perfectly adequate when the Internet was small.
However, as more people, devices, and services connected online, IPv4’s supply of addresses could no longer keep up with the growth. This shortage triggered the introduction of temporary workarounds and long-term solutions — the most significant being Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) and IPv6.
To extend the lifespan of IPv4, many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) adopted Carrier-Grade NAT. Instead of assigning every user a unique public IP address, CGNAT enables multiple customers to share a single IP. Each household receives a private internal address, and a translation layer maps internal traffic to the shared public IP.
This approach successfully delayed IPv4 exhaustion, but it introduced several limitations. CGNAT disrupts the Internet’s original end-to-end communication model by placing translation devices in the middle of user connections. As a consequence, certain applications struggle to function correctly, especially those that rely on direct connectivity.
Port forwarding becomes extremely difficult, sometimes impossible. This affects use cases such as home servers, online gaming, peer-to-peer applications, remote access setups, and more. Additionally, when multiple users share the same public IP, identifying the source of spam, abuse, or cyberattacks becomes far more complex. These challenges make CGNAT a useful but imperfect solution.
IPv6 was created as a permanent and future-proof alternative to IPv4. With its 128-bit address space, IPv6 provides an enormous pool of unique public addresses — enough for every device on Earth and many more.
Unlike CGNAT-based IPv4 setups, IPv6 supports true end-to-end connectivity. Every device can be globally reachable without relying on NAT layers or port mapping workarounds. This leads to cleaner network designs, lower complexity, improved reliability, and better performance for applications that require direct communication.
Despite its advantages, IPv6 adoption has been slower than expected. Many networks still run primarily on IPv4 infrastructure, and not all devices or applications fully support IPv6. In some cases, IPv6 is deployed using the same philosophies as IPv4 NAT, reducing the benefits of the protocol due to outdated design assumptions.
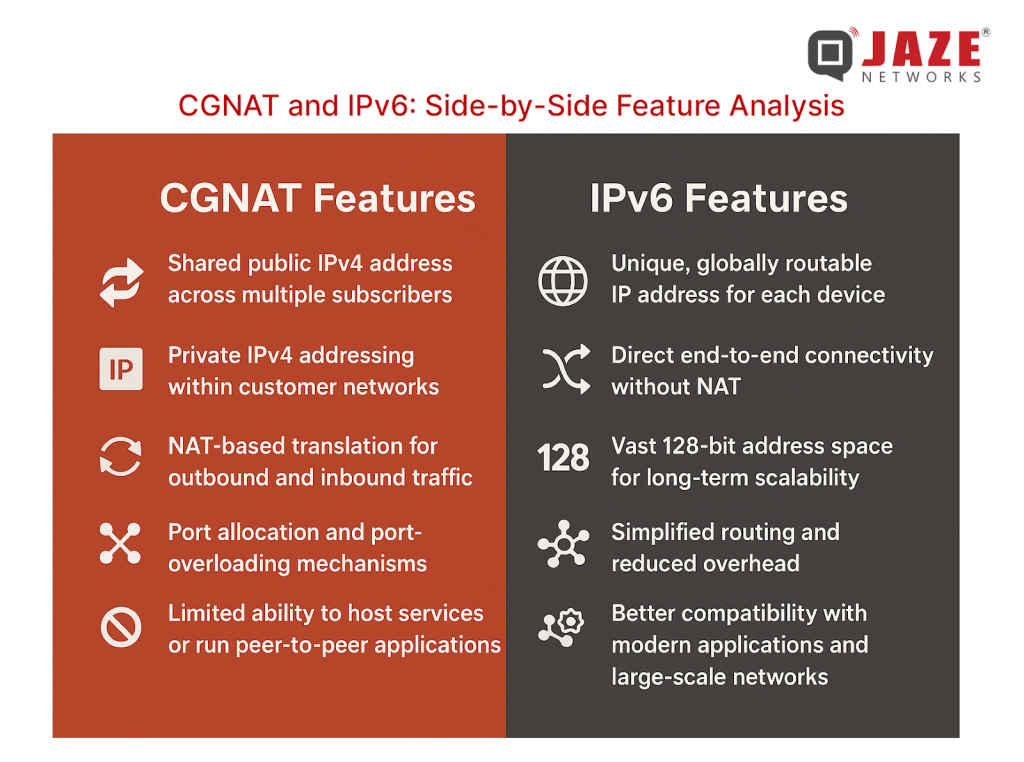
The differences between CGNAT and IPv6 become clear when examining common real-world scenarios:
In essence, CGNAT introduces friction for modern, interactive Internet use cases, while IPv6 aligns naturally with today’s connectivity needs.
Migrating an entire global Internet ecosystem is complex. Several factors slow down IPv6 deployment:
To move forward, ISPs must embrace native IPv6 routing instead of leaning on NAT-based stopgaps. Device manufacturers and service providers should treat IPv6 compatibility as mandatory, not optional. Developers and technical professionals need to adopt IPv6-first design principles to ensure smooth interoperability.
CGNAT has played an important role in extending the life of IPv4, but its limitations are increasingly apparent. It complicates connectivity, affects performance, reduces transparency, and restricts how users interact with the Internet.
IPv6, by contrast, provides scalability, efficiency, and true end-to-end communication — all essential for the modern digital ecosystem. While the transition is ongoing, IPv6 represents the Internet’s long-term foundation.
For users who rely on hosting, gaming, remote access, or advanced networking features, choosing an ISP that offers robust, native IPv6 routing can significantly improve their experience. For technology creators and providers, adopting IPv6-first development ensures long-term compatibility and reliability.
Ultimately, the future of the Internet is built on abundant addressing, simplified routing, and open connectivity — the principles that IPv6 was designed to deliver.
Jaze ISP Manager offers comprehensive solutions to help ISPs transition seamlessly to IPv6 with integration with all major BNG providers ensuring robust network performance and future-proof connectivity.
API (Application Programming Interface) integration allows different software applications to exchange information seamlessly—and that matters a lot for Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
Consider this scenario: A new subscriber signs up via your mobile app, their account is created in your billing system, the network gateway provisions their service, and the CRM logs the sale—all in real time. Without API integration, this flow involves manual steps, delays, errors, and lots of overhead. With it, everything happens automatically.
For ISPs, that means faster onboarding, fewer customer issues, lower operational costs, and better scalability. As access technologies diversify (fiber, WiFi 6/7, fixed-wireless, IPTV, OTT), the number of connected systems grows—but so does the need for smooth, automated data flow. API integration isn’t just “nice to have”—it’s a competitive necessity.

At its simplest: application A sends a request, application B responds. Under the hood, there are a few key elements:
In practical terms for ISPs: your customer portal might call an API to create a subscriber record; your billing engine might call another API to update plan status; your network controller might call an API to configure network access. Each of these steps is automated and connected.
For ISPs, choosing the right method depends on scale, variety of systems, and how fast you need to move. As your ecosystem grows (multiple access types, value-added services, OTT bundles), an iPaaS-style approach tends to make the most sense.
API integrations offer a wide range of benefits—here are some key use cases:
Delayed or fragmented integrations cost ISPs far more than just slow processes. They cost growth, customer satisfaction, and innovation. In today’s broadband-hungry world, seamless API integration is no longer optional—it’s mission-critical.
If you’re an ISP looking to scale, diversify services, and reduce operational overhead, make API integration a key pillar of your strategy. It’s the connective tissue that lets all your tools—billing, network, CRM, OTT, payments—work as one.

Click here to learn more.
The broadband era has surged ahead. With streaming, IoT, remote work and fixed-wireless access all increasing, the role of the Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) is more critical than ever. What used to be a fairly straightforward gateway for customer broadband access is now the core pivot in ISP networks — managing subscriber sessions, enforcing policy, enabling new services.
As ISPs and software providers look ahead, it’s timely to review how BNG access models are evolving — what the new models are, why they matter, and what to consider when redefining your architecture.
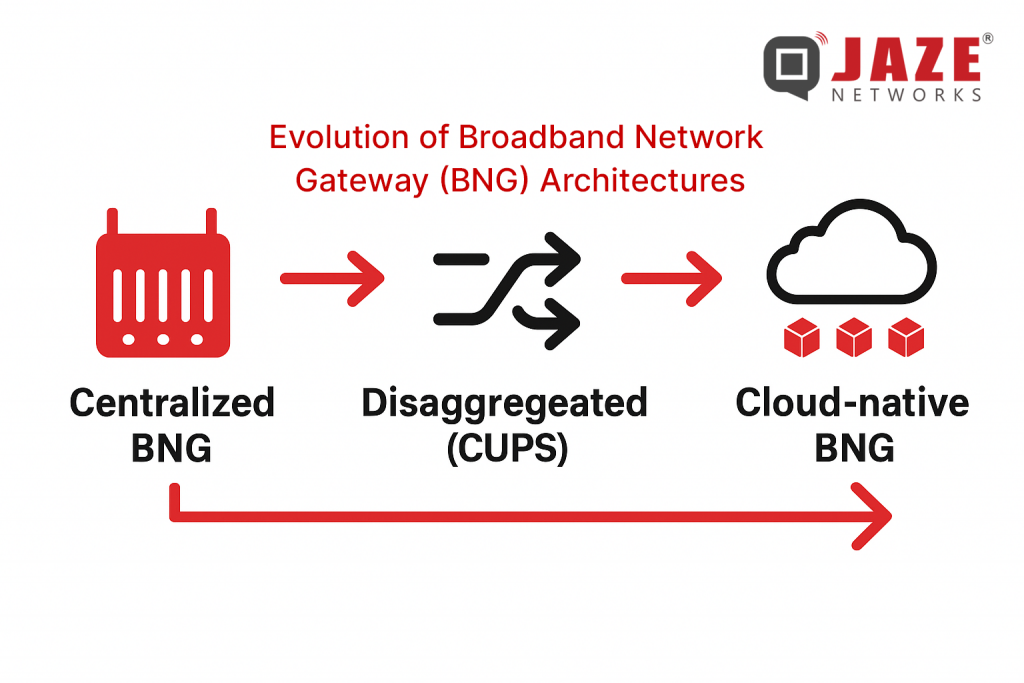
Older BNG architectures were largely built around these characteristics:
However, several shifts are making this traditional model less effective:
Because of this, ISPs must rethink the BNG — the access model, deployment location, and software vs hardware trade-offs.
Here are several access models emerging in the BNG space — useful to understand for product positioning, network architecture or software service strategy:
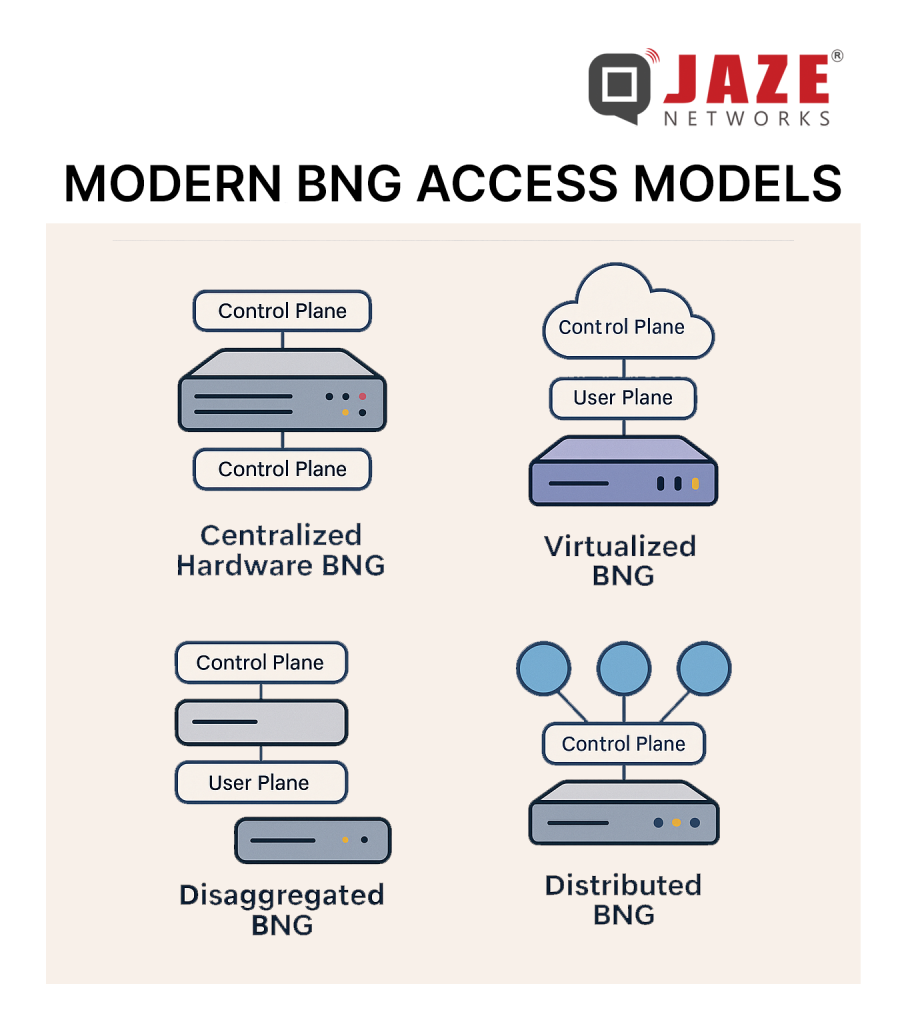
From the vantage of an ISP or a software vendor for ISPs, understanding these access models gives you strategic insight:
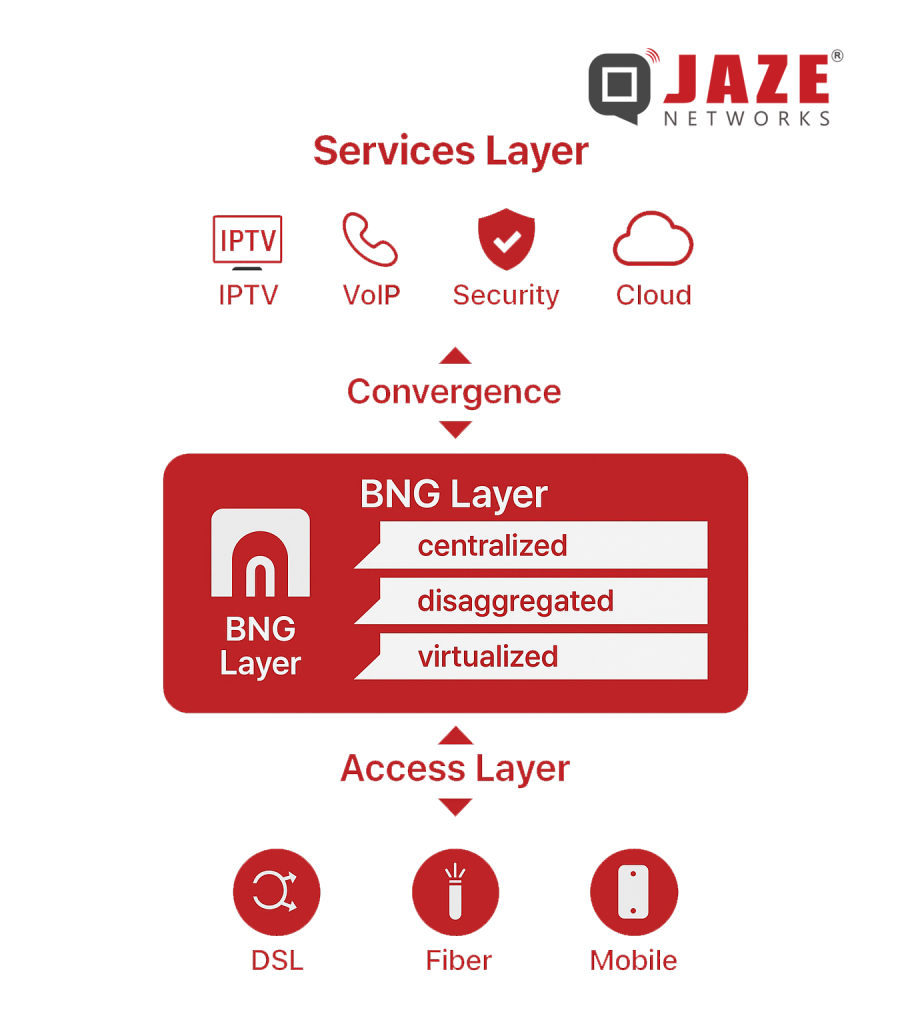
Cost efficiency & scalability: Virtualised/disaggregated BNGs reduce hardware dependency, enable scaling with demand, lower OPEX.
Service agility: Faster introduction of new pricing tiers, service bundles, new access types (FWA, WiFi) — software control matters.
Operational simplicity: Central control plane means fewer edge-appliances to manage; disaggregation means upgrades, scaling becomes less disruptive.
Edge performance & user experience: With distributed user plane, latency and backhaul loads are reduced, supporting high-quality real-time services.
Convergence & future-proofing: Fixed + wireless + multi-access handled by common architecture means ISPs are better positioned for 5G, IoT, edge-services.
Here’s a quick checklist for ISPs and software vendors to assess their BNG strategy:
Subscriber scale & growth: Can the model scale out linearly with subscriber growth and traffic loads?
Access diversity: Will your access types (fiber, FWA, WiFi) be supported under the model?
Control vs user plane location: How decoupled are they? Where will user plane be located for optimal performance?
Software orchestration & automation: Are provisioning, policy, subscriber lifecycle fully automated?
Service agility: How quickly can new tariff plans, bundles, access services be introduced?
Hardware dependency: What is the capex/opex trade-off? Can you move toward software-defined alternatives?
Edge readiness & latency: If you support real-time or OTT services, is your user plane close enough to the edge?
Vendor ecosystem & integration: Does the solution support open interfaces, multi-vendor, easier upgrades?
Whether you go for a centralised appliance, a virtualised cloud-native gateway, a disaggregated CUPS architecture or an edge-distributed model — the common theme is flexibility, software-first, multi-access readiness and subscriber-centric policy control. For ISPs and the SaaS companies that serve them, aligning your strategy (and your software platform) with these modern BNG access models means you’re not just keeping up — you’re positioning for next-gen broadband services, better user experience and operational advantage.
Jaze ISP Manager offers seamless integration with leading BNG/BRAS platforms — enabling ISPs to manage subscriber sessions, enforce policy across all access types, automate provisioning and billing, and monitor network health from one unified dashboard. Whether you are operating a traditional hardware BNG, moving to virtualised models or adopting a distributed edge architecture, Jaze ISP Manager supports the full lifecycle: from onboarding to churn, with scalability built in.
Click here to learn more.
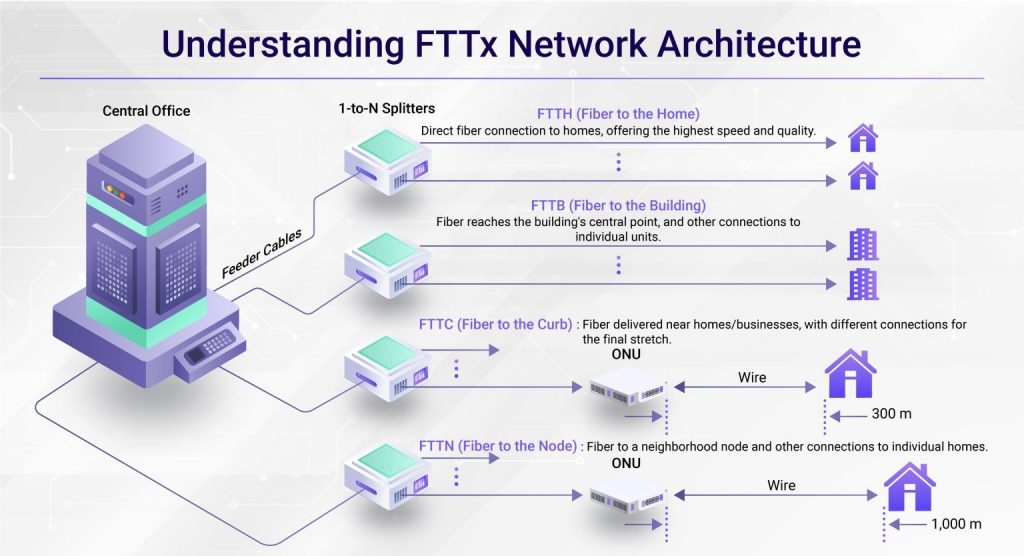
Fiber to the X (FTTX) is more than just a buzzword; it represents a fundamental shift in how we connect to the digital world. It is the general term for any broadband network architecture that replaces all or part of the traditional metal local loop with high-capacity optical fiber. The “X” in FTTX signifies the various termination points—whether it’s the home (FTTH), building (FTTB), curb (FTTC), or node (FTTN)—each step closer to the end-user dramatically improves the quality of service.
The move to FTTX is driven by fiber optics’ inherent superiority over copper cable, offering unparalleled performance benefits that are critical for modern digital life:
High Bandwidth: Optical fibers can transmit exponentially more data than copper, easily supporting high-speed internet, 4K/8K streaming, and data-intensive cloud applications without bottlenecks.
Future-Proofing: Fiber networks have a remarkably long lifespan and are inherently scalable. Upgrading is often as simple as changing the electronics at the end points, ensuring the network can support ever-increasing data rates for decades to come.
Low Latency: Data transmission via light provides extremely low latency, which is essential for real-time applications like competitive online gaming, high-definition video conferencing, and mission-critical cloud-based operations.
Superior Reliability: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference and less susceptible to environmental factors like moisture and temperature swings, resulting in more stable and consistent service delivery.
Driving Real-World Applications
The deployment of FTTX is fueling innovation across every sector:
Residential Broadband (FTTH): Fiber to the Home delivers the highest speeds and quality directly to consumers, powering smart homes and supporting multiple simultaneous users and high-demand applications.
Business Connectivity (FTTB): Fiber reaches a building’s central point, providing businesses with the reliable, high-speed services crucial for modern operations, data backups, and multi-site connectivity.
Smart Cities & Education: FTTX acts as the nervous system for smart city infrastructure, supporting everything from traffic management to public safety systems. It also enables high-speed connectivity for educational institutions, fostering e-learning and advanced research.
The global adoption of FTTX solidifies fiber as the undisputed standard for modern connectivity. For Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network operators, the challenge now shifts from deploying fiber to optimizing its operation and managing its subscribers at scale. Success in this new landscape hinges on having a management platform that can handle the sheer volume and complexity of a high-capacity fiber network while streamlining operations.
To truly capitalize on your fiber investment and maximize both network performance and profitability, the path forward requires next-generation intelligence.
With Jaze ISP Manager, you gain a comprehensive, end-to-end operational platform specifically built for the modern fiber provider. This solution transforms operational complexity into seamless efficiency by automating everything from subscriber lifecycle and flexible billing to network provisioning and quality of service (QoS) management.
Don’t let the complexity of managing a large-scale fiber network undermine your competitive edge. Empower your FTTX business with the unified, scalable intelligence of Jaze ISP Manager to guarantee superior quality of experience for your customers and ensure sustainable growth in the fiber-powered future.
When we talk about internet speed, most people instantly think about how fast they can download movies, stream videos, or browse social media. But in today’s world, it’s not just about downloading anymore — upload speed is equally important.
As we step into 2025–2026, when remote work, cloud storage, video creation, and smart devices dominate daily life, upload speed can make or break your digital experience.
Let’s understand why it matters — and how it affects almost everything you do online.
What Exactly Is Upload Speed?
Upload speed refers to how quickly you can send data from your device to the internet.
It’s measured in megabits per second (Mbps), just like download speed.
Every time you:
—you’re using your upload bandwidth.
If your upload speed is low, even a strong download connection can feel sluggish or unstable during these tasks.
1. The Era of Remote Work & Online Collaboration
Work-from-home and hybrid models are here to stay. Every video meeting, shared file, or cloud document relies on your upload connection.
A slow upload speed means blurry video calls, lagging audio, and constant “reconnecting…” messages — not ideal when you’re presenting to clients or attending classes online.
2. Social Media & Content Creation Boom
From influencers to small business owners, everyone is uploading photos, reels, and videos daily.
With 4K and 8K becoming standard, files are huge. High upload speed ensures your videos go live faster — and without frustrating delays.
3. Cloud Storage & Backup
We’re moving away from storing everything on devices. Automatic backups to Google Photos, iCloud, and OneDrive constantly use upload bandwidth.
If upload speeds are low, backups slow down, sync fails, and your data may remain outdated.
4. Smart Homes & IoT Devices
Cameras, sensors, and voice assistants send continuous data to cloud servers.
When upload bandwidth is insufficient, you’ll see camera feed delays, failed device syncs, or unreliable smart automation.
5. Gaming & Live Streaming
Gamers know the pain of lag.Online gaming and live streaming both rely on strong upstream connections — every action, every frame, every voice chat goes out through your upload channel.
Higher upload speeds mean smoother gameplay and crystal-clear streams.
| Online Activity | Recommended Upload Speed |
| Video calls (Zoom, Meet) | 3–5 Mbps |
| Cloud backups | 10–20 Mbps |
| Online gaming | 5–10 Mbps |
| 4K live streaming | 20–25 Mbps |
| Uploading large media files | 25 Mbps and above |
If multiple devices or users share the same connection, you’ll need even higher speeds for a seamless experience.

India’s internet usage pattern is shifting fast. Earlier, most users were consumers of content — watching, downloading, or streaming.
But now, millions are creators — students uploading projects, professionals hosting webinars, and entrepreneurs managing online stores.
Unfortunately, many broadband plans in India still prioritize download speeds and offer much lower uploads (often just 10–20% of download rates).
That imbalance is slowly changing, as fiber networks and symmetrical connections become mainstream.
Traditional broadband (like copper or DSL) can’t handle equal upload and download speeds.
But fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) connections deliver symmetrical speeds — meaning if you get 200 Mbps download, you also get 200 Mbps upload.
This makes a huge difference for:
Fiber technology is the backbone of India’s digital growth — and it’s finally bridging the upload gap.
As India embraces a creator-driven digital economy, upload speed is no longer secondary — it’s essential.
Whether you’re working from home, managing an online business, or sharing your creativity with the world, faster upload speeds ensure smoother, smarter, and more reliable connectivity.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs by optimising bandwidth delivery and provide a seamless experience to subscribers. This ensures stable upload speeds for users, reduces congestion during peak hours, and improves performance for video calls, cloud backups, and live streaming. In short, it gives ISPs the tools to maintain reliable upstream performance for their customers. Click here to know more
Real-Time Communications (RTC) — whether video conferencing, live streaming, or VoIP — have become the backbone of modern connectivity. Users expect instant, uninterrupted interaction, and even minor delays can cause frustration. Delivering this level of performance requires more than just fast internet; it relies on understanding Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE), and how they intersect.
Quality of Service (QoS) is the technical engine that ensures RTC traffic moves efficiently across networks. Without it, calls drop, video lags, and user frustration rises.
Key QoS mechanisms include:
By controlling these network variables, QoS provides measurable reliability — the foundation for any RTC application.
While QoS handles the network, Quality of Experience (QoE) focuses on how users perceive the service. High network performance doesn’t automatically translate into a satisfying experience if the application is difficult to use or inconsistent.
Factors affecting QoE include:
Measuring QoE often involves subjective feedback, such as Mean Opinion Scores (MOS), surveys, or session success rates.
The most successful RTC experiences occur when QoS and QoE are aligned. Network optimizations (QoS) set the stage, but user perception (QoE) determines satisfaction.
For instance, a video conference may have excellent packet delivery, low latency, and zero jitter — but if users struggle to navigate the app or experience confusing error messages, QoE suffers.
Integrated monitoring of both QoS metrics (latency, jitter, packet loss) and QoE indicators (MOS, user engagement) allows providers to proactively identify problems and enhance the overall experience.
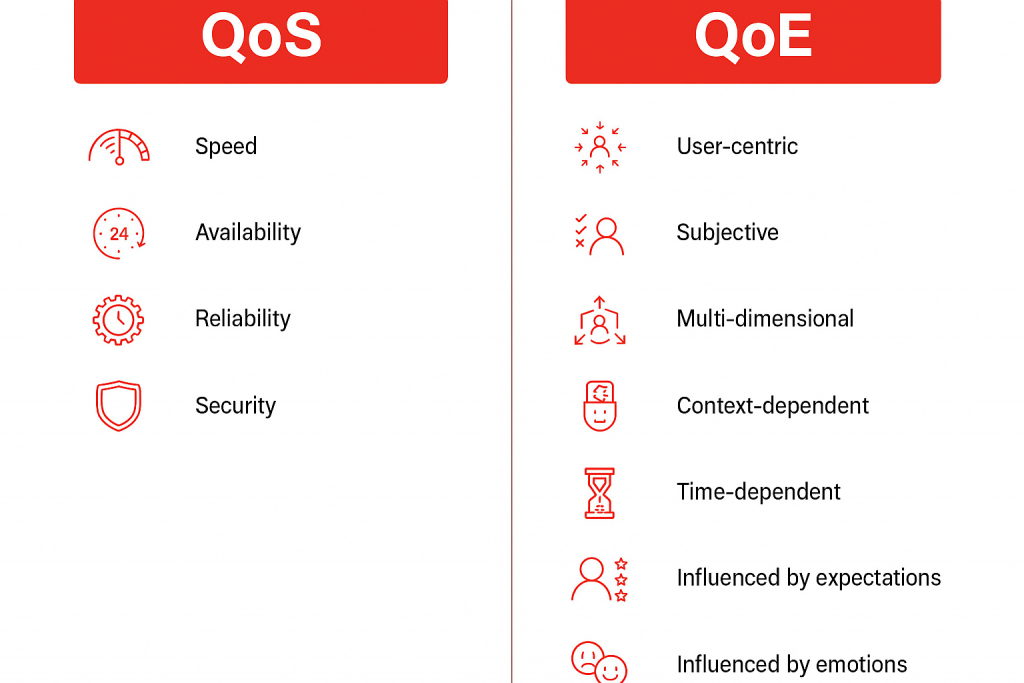
Monitoring the right metrics helps bridge technical performance and user satisfaction:
QoS Metrics:
QoE Metrics:
Tracking both sets of metrics ensures service providers can pinpoint issues, whether technical or user-facing.
These strategies provide measurable improvements in both technical performance and user satisfaction.
In a digital-first world, RTC performance can make or break user experiences. QoS ensures the network can deliver real-time data reliably, while QoE measures the perception and satisfaction of the user. Service providers who monitor, optimize, and balance both aspects will not only prevent disruptions but also build trust and loyalty among their users.
Investing in QoS and QoE is not optional — it’s the foundation for RTC success, whether in business, education, or everyday social interactions.
Jaze ISP Manager becomes critical in this equation. In integration with BNG providers, Jaze ISP Manager automates enforcement of intelligent traffic policies, and provides real-time analytics, empowering ISPs to deliver consistent QoS while keeping QoE at the center. The result: seamless RTC experiences, satisfied subscribers, and a future-ready network that scales effortlessly with demand.
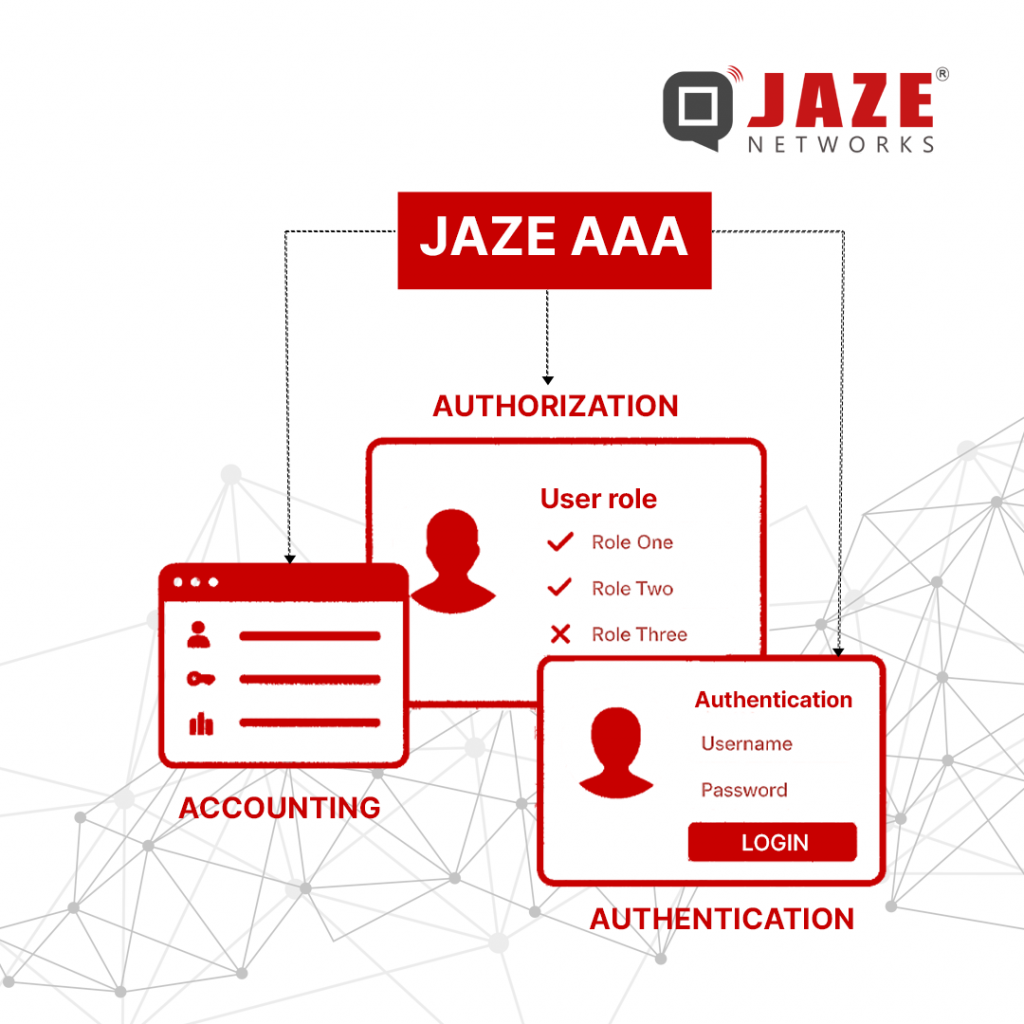
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and enterprises face mounting pressure to secure their networks while ensuring seamless user experiences in the fast-paced digital era. The Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) framework provides a structured approach to manage network access, prevent misuse, and maintain compliance.
AAA stands for:
Together, these three processes create a reliable system that ensures only the right people get the right level of access—while all activities are logged for accountability.
Unauthorized access can lead to service abuse, downtime, and regulatory risks. AAA protocols ensure only verified users connect to the network, reducing threats from both external attackers and internal misuse.
With authorization policies, ISPs can assign access levels based on roles—customers, staff, or partners—ensuring sensitive systems remain protected.
Accounting helps providers monitor how network resources are used. For ISPs, this is especially valuable for bandwidth management, billing accuracy, and detecting unusual traffic spikes.
Governments and regulators demand traceability of network activity. Accounting logs serve as digital evidence to meet compliance requirements and reassure customers about data security.
Different protocols implement AAA in unique ways. Here are the most widely adopted:
For ISPs and large businesses, a well-structured AAA setup is critical. The implementation usually involves:
To get the most out of AAA frameworks, operators should:
As ISPs expand services into fiber, 5G, and enterprise networking, the demand for scalable, automated AAA systems will only grow. Cloud-native AAA platforms are already emerging, offering flexibility and real-time policy enforcement across distributed infrastructures.
For ISPs and enterprises alike, AAA is no longer optional—it’s the foundation of secure, reliable, and accountable network access. By choosing the right protocols, enforcing strong access policies, and embracing best practices, operators can strengthen security, streamline operations, and build customer trust.
Jaze ISP Manager delivers carrier-grade AAA with centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting to secure broadband, enterprise, and public access networks. It integrates seamlessly with RADIUS and TACACS+ for subscriber management and device administration across distributed infrastructures.
ISPs can enforce role-based access policies, streamline user onboarding, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Built-in redundancy guarantees high availability, while real-time accounting provides transparency for usage, billing, and auditing. By combining automation with AAA architecture, Jaze enables operators to deliver uninterrupted connectivity, faster troubleshooting, and reliable service at scale.
Click here to know more