




The Internet today works much like a vast and rapidly expanding city. Every device — whether it’s your phone, laptop, or home router — needs a unique address to send and receive information. For decades, this addressing system depended on IPv4, a 32-bit structure that was perfectly adequate when the Internet was small.
However, as more people, devices, and services connected online, IPv4’s supply of addresses could no longer keep up with the growth. This shortage triggered the introduction of temporary workarounds and long-term solutions — the most significant being Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) and IPv6.
To extend the lifespan of IPv4, many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) adopted Carrier-Grade NAT. Instead of assigning every user a unique public IP address, CGNAT enables multiple customers to share a single IP. Each household receives a private internal address, and a translation layer maps internal traffic to the shared public IP.
This approach successfully delayed IPv4 exhaustion, but it introduced several limitations. CGNAT disrupts the Internet’s original end-to-end communication model by placing translation devices in the middle of user connections. As a consequence, certain applications struggle to function correctly, especially those that rely on direct connectivity.
Port forwarding becomes extremely difficult, sometimes impossible. This affects use cases such as home servers, online gaming, peer-to-peer applications, remote access setups, and more. Additionally, when multiple users share the same public IP, identifying the source of spam, abuse, or cyberattacks becomes far more complex. These challenges make CGNAT a useful but imperfect solution.
IPv6 was created as a permanent and future-proof alternative to IPv4. With its 128-bit address space, IPv6 provides an enormous pool of unique public addresses — enough for every device on Earth and many more.
Unlike CGNAT-based IPv4 setups, IPv6 supports true end-to-end connectivity. Every device can be globally reachable without relying on NAT layers or port mapping workarounds. This leads to cleaner network designs, lower complexity, improved reliability, and better performance for applications that require direct communication.
Despite its advantages, IPv6 adoption has been slower than expected. Many networks still run primarily on IPv4 infrastructure, and not all devices or applications fully support IPv6. In some cases, IPv6 is deployed using the same philosophies as IPv4 NAT, reducing the benefits of the protocol due to outdated design assumptions.
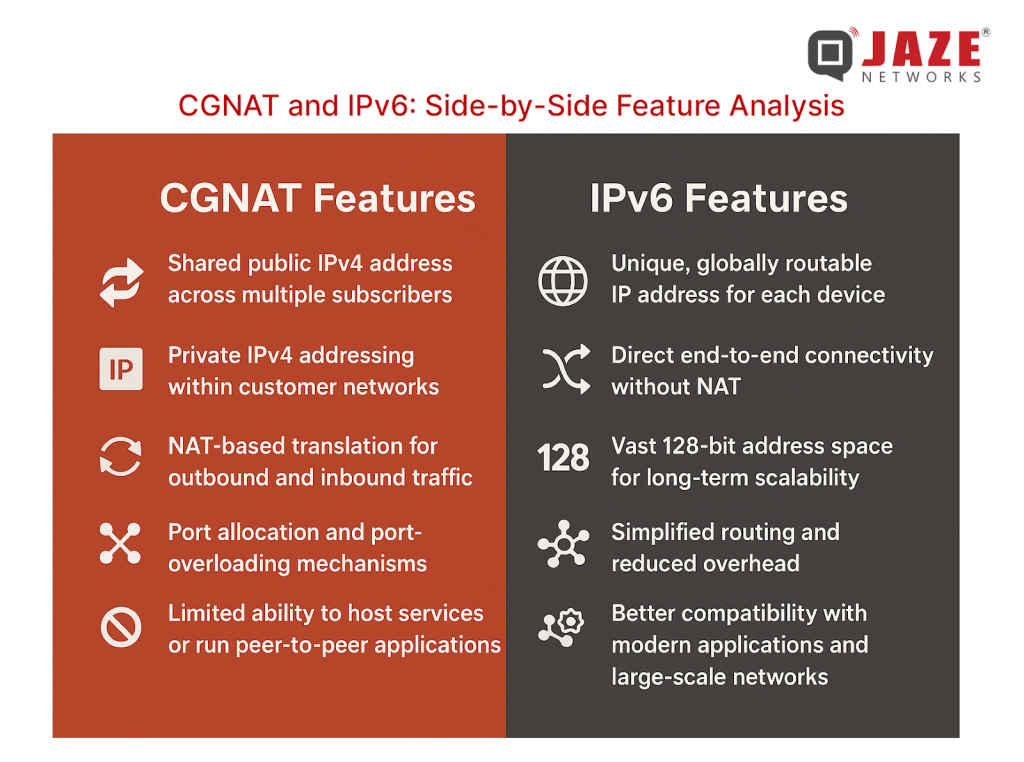
The differences between CGNAT and IPv6 become clear when examining common real-world scenarios:
In essence, CGNAT introduces friction for modern, interactive Internet use cases, while IPv6 aligns naturally with today’s connectivity needs.
Migrating an entire global Internet ecosystem is complex. Several factors slow down IPv6 deployment:
To move forward, ISPs must embrace native IPv6 routing instead of leaning on NAT-based stopgaps. Device manufacturers and service providers should treat IPv6 compatibility as mandatory, not optional. Developers and technical professionals need to adopt IPv6-first design principles to ensure smooth interoperability.
CGNAT has played an important role in extending the life of IPv4, but its limitations are increasingly apparent. It complicates connectivity, affects performance, reduces transparency, and restricts how users interact with the Internet.
IPv6, by contrast, provides scalability, efficiency, and true end-to-end communication — all essential for the modern digital ecosystem. While the transition is ongoing, IPv6 represents the Internet’s long-term foundation.
For users who rely on hosting, gaming, remote access, or advanced networking features, choosing an ISP that offers robust, native IPv6 routing can significantly improve their experience. For technology creators and providers, adopting IPv6-first development ensures long-term compatibility and reliability.
Ultimately, the future of the Internet is built on abundant addressing, simplified routing, and open connectivity — the principles that IPv6 was designed to deliver.
Jaze ISP Manager offers comprehensive solutions to help ISPs transition seamlessly to IPv6 with integration with all major BNG providers ensuring robust network performance and future-proof connectivity.
API (Application Programming Interface) integration allows different software applications to exchange information seamlessly—and that matters a lot for Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
Consider this scenario: A new subscriber signs up via your mobile app, their account is created in your billing system, the network gateway provisions their service, and the CRM logs the sale—all in real time. Without API integration, this flow involves manual steps, delays, errors, and lots of overhead. With it, everything happens automatically.
For ISPs, that means faster onboarding, fewer customer issues, lower operational costs, and better scalability. As access technologies diversify (fiber, WiFi 6/7, fixed-wireless, IPTV, OTT), the number of connected systems grows—but so does the need for smooth, automated data flow. API integration isn’t just “nice to have”—it’s a competitive necessity.

At its simplest: application A sends a request, application B responds. Under the hood, there are a few key elements:
In practical terms for ISPs: your customer portal might call an API to create a subscriber record; your billing engine might call another API to update plan status; your network controller might call an API to configure network access. Each of these steps is automated and connected.
For ISPs, choosing the right method depends on scale, variety of systems, and how fast you need to move. As your ecosystem grows (multiple access types, value-added services, OTT bundles), an iPaaS-style approach tends to make the most sense.
API integrations offer a wide range of benefits—here are some key use cases:
Delayed or fragmented integrations cost ISPs far more than just slow processes. They cost growth, customer satisfaction, and innovation. In today’s broadband-hungry world, seamless API integration is no longer optional—it’s mission-critical.
If you’re an ISP looking to scale, diversify services, and reduce operational overhead, make API integration a key pillar of your strategy. It’s the connective tissue that lets all your tools—billing, network, CRM, OTT, payments—work as one.

Click here to learn more.
The broadband era has surged ahead. With streaming, IoT, remote work and fixed-wireless access all increasing, the role of the Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) is more critical than ever. What used to be a fairly straightforward gateway for customer broadband access is now the core pivot in ISP networks — managing subscriber sessions, enforcing policy, enabling new services.
As ISPs and software providers look ahead, it’s timely to review how BNG access models are evolving — what the new models are, why they matter, and what to consider when redefining your architecture.
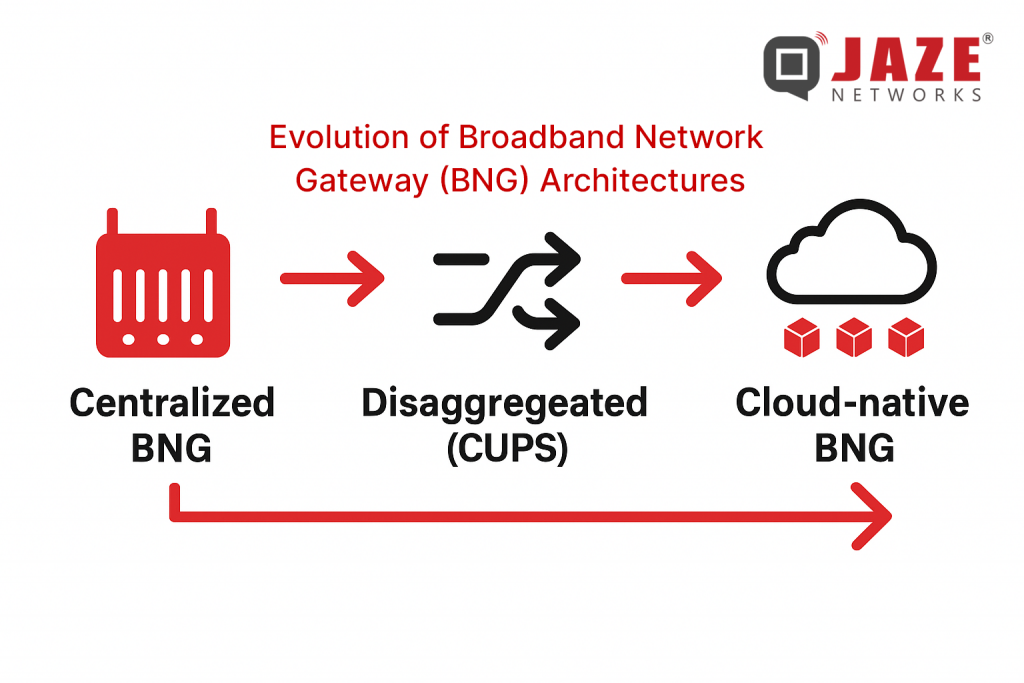
Older BNG architectures were largely built around these characteristics:
However, several shifts are making this traditional model less effective:
Because of this, ISPs must rethink the BNG — the access model, deployment location, and software vs hardware trade-offs.
Here are several access models emerging in the BNG space — useful to understand for product positioning, network architecture or software service strategy:
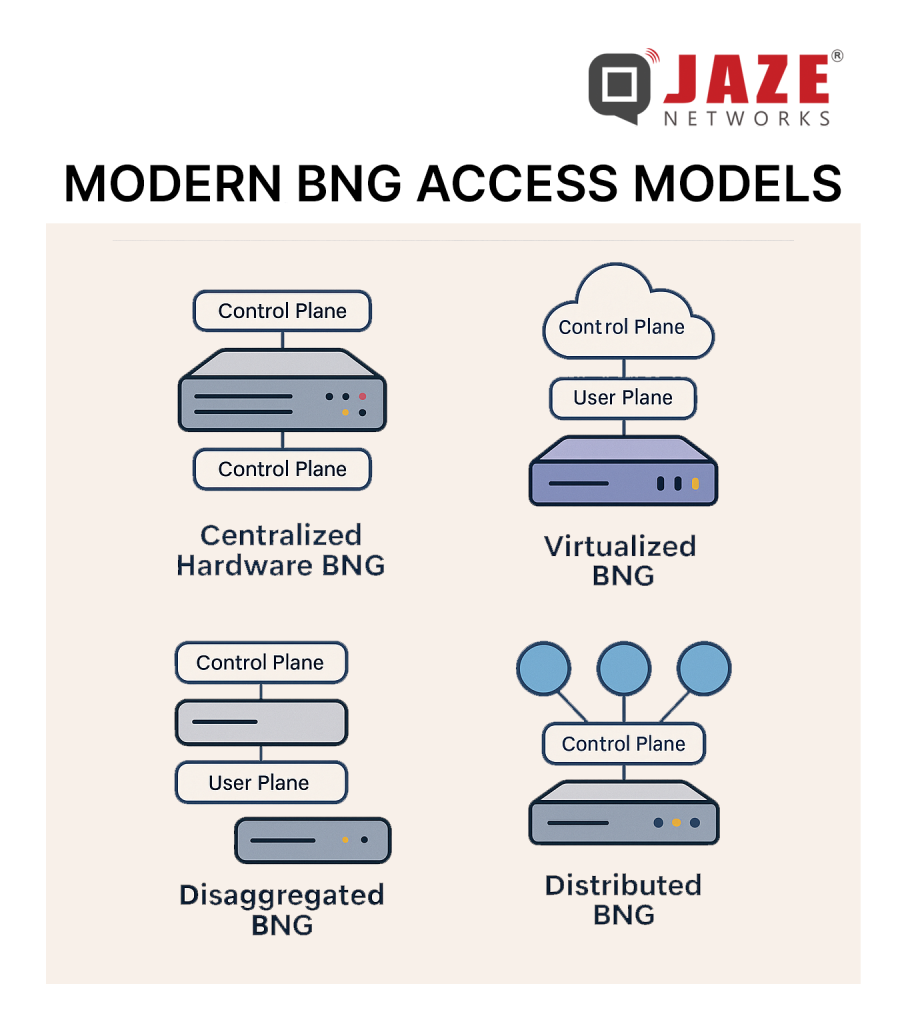
From the vantage of an ISP or a software vendor for ISPs, understanding these access models gives you strategic insight:
Cost efficiency & scalability: Virtualised/disaggregated BNGs reduce hardware dependency, enable scaling with demand, lower OPEX.
Service agility: Faster introduction of new pricing tiers, service bundles, new access types (FWA, WiFi) — software control matters.
Operational simplicity: Central control plane means fewer edge-appliances to manage; disaggregation means upgrades, scaling becomes less disruptive.
Edge performance & user experience: With distributed user plane, latency and backhaul loads are reduced, supporting high-quality real-time services.
Convergence & future-proofing: Fixed + wireless + multi-access handled by common architecture means ISPs are better positioned for 5G, IoT, edge-services.
Here’s a quick checklist for ISPs and software vendors to assess their BNG strategy:
Subscriber scale & growth: Can the model scale out linearly with subscriber growth and traffic loads?
Access diversity: Will your access types (fiber, FWA, WiFi) be supported under the model?
Control vs user plane location: How decoupled are they? Where will user plane be located for optimal performance?
Software orchestration & automation: Are provisioning, policy, subscriber lifecycle fully automated?
Service agility: How quickly can new tariff plans, bundles, access services be introduced?
Hardware dependency: What is the capex/opex trade-off? Can you move toward software-defined alternatives?
Edge readiness & latency: If you support real-time or OTT services, is your user plane close enough to the edge?
Vendor ecosystem & integration: Does the solution support open interfaces, multi-vendor, easier upgrades?
Whether you go for a centralised appliance, a virtualised cloud-native gateway, a disaggregated CUPS architecture or an edge-distributed model — the common theme is flexibility, software-first, multi-access readiness and subscriber-centric policy control. For ISPs and the SaaS companies that serve them, aligning your strategy (and your software platform) with these modern BNG access models means you’re not just keeping up — you’re positioning for next-gen broadband services, better user experience and operational advantage.
Jaze ISP Manager offers seamless integration with leading BNG/BRAS platforms — enabling ISPs to manage subscriber sessions, enforce policy across all access types, automate provisioning and billing, and monitor network health from one unified dashboard. Whether you are operating a traditional hardware BNG, moving to virtualised models or adopting a distributed edge architecture, Jaze ISP Manager supports the full lifecycle: from onboarding to churn, with scalability built in.
Click here to learn more.
When we talk about internet speed, most people instantly think about how fast they can download movies, stream videos, or browse social media. But in today’s world, it’s not just about downloading anymore — upload speed is equally important.
As we step into 2025–2026, when remote work, cloud storage, video creation, and smart devices dominate daily life, upload speed can make or break your digital experience.
Let’s understand why it matters — and how it affects almost everything you do online.
What Exactly Is Upload Speed?
Upload speed refers to how quickly you can send data from your device to the internet.
It’s measured in megabits per second (Mbps), just like download speed.
Every time you:
—you’re using your upload bandwidth.
If your upload speed is low, even a strong download connection can feel sluggish or unstable during these tasks.
1. The Era of Remote Work & Online Collaboration
Work-from-home and hybrid models are here to stay. Every video meeting, shared file, or cloud document relies on your upload connection.
A slow upload speed means blurry video calls, lagging audio, and constant “reconnecting…” messages — not ideal when you’re presenting to clients or attending classes online.
2. Social Media & Content Creation Boom
From influencers to small business owners, everyone is uploading photos, reels, and videos daily.
With 4K and 8K becoming standard, files are huge. High upload speed ensures your videos go live faster — and without frustrating delays.
3. Cloud Storage & Backup
We’re moving away from storing everything on devices. Automatic backups to Google Photos, iCloud, and OneDrive constantly use upload bandwidth.
If upload speeds are low, backups slow down, sync fails, and your data may remain outdated.
4. Smart Homes & IoT Devices
Cameras, sensors, and voice assistants send continuous data to cloud servers.
When upload bandwidth is insufficient, you’ll see camera feed delays, failed device syncs, or unreliable smart automation.
5. Gaming & Live Streaming
Gamers know the pain of lag.Online gaming and live streaming both rely on strong upstream connections — every action, every frame, every voice chat goes out through your upload channel.
Higher upload speeds mean smoother gameplay and crystal-clear streams.
| Online Activity | Recommended Upload Speed |
| Video calls (Zoom, Meet) | 3–5 Mbps |
| Cloud backups | 10–20 Mbps |
| Online gaming | 5–10 Mbps |
| 4K live streaming | 20–25 Mbps |
| Uploading large media files | 25 Mbps and above |
If multiple devices or users share the same connection, you’ll need even higher speeds for a seamless experience.

India’s internet usage pattern is shifting fast. Earlier, most users were consumers of content — watching, downloading, or streaming.
But now, millions are creators — students uploading projects, professionals hosting webinars, and entrepreneurs managing online stores.
Unfortunately, many broadband plans in India still prioritize download speeds and offer much lower uploads (often just 10–20% of download rates).
That imbalance is slowly changing, as fiber networks and symmetrical connections become mainstream.
Traditional broadband (like copper or DSL) can’t handle equal upload and download speeds.
But fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) connections deliver symmetrical speeds — meaning if you get 200 Mbps download, you also get 200 Mbps upload.
This makes a huge difference for:
Fiber technology is the backbone of India’s digital growth — and it’s finally bridging the upload gap.
As India embraces a creator-driven digital economy, upload speed is no longer secondary — it’s essential.
Whether you’re working from home, managing an online business, or sharing your creativity with the world, faster upload speeds ensure smoother, smarter, and more reliable connectivity.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs by optimising bandwidth delivery and provide a seamless experience to subscribers. This ensures stable upload speeds for users, reduces congestion during peak hours, and improves performance for video calls, cloud backups, and live streaming. In short, it gives ISPs the tools to maintain reliable upstream performance for their customers. Click here to know more
The demand for high-speed internet is growing exponentially, fueled by the rise of 8K streaming, IoT, and cloud applications. Traditional fiber rollouts, while effective, can be costly and time-consuming, especially in suburban and semi-urban areas. Enter MicroPoPs (Micro Point of Presence)—a game-changer for ISPs looking to maximize fiber efficiency while expanding network reach.
What Are MicroPoPs?
MicroPoPs are small-scale, fiber-fed network nodes that act as local distribution points for high-speed broadband services. Unlike conventional fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments that extend fiber all the way to individual residences, MicroPoPs bring fiber close to end-users while leveraging high-capacity wireless or last-mile fiber solutions to complete the connection.
The Role of MicroPoPs in ISP Networks
MicroPoPs are strategically placed within a community to deliver gigabit-capable speeds over a short distance. By deploying MicroPoPs, ISPs can efficiently utilize their fiber backbone while minimizing expensive trenching and infrastructure costs.
Here’s how they fit into modern ISP architectures:
Fiber Backbone Integration – MicroPoPs are connected to an ISP’s core network via regional fiber hubs or aggregation points, ensuring high-speed data transmission.
High-Bandwidth Distribution – From a MicroPoP, ISPs can deploy Fiber-to-the-Curb (FTTC), Fiber-to-the-Building (FTTB), or hybrid fiber-wireless models to serve multiple subscribers.
Reduced Latency & Congestion – By placing data processing closer to users, MicroPoPs improve network efficiency, reducing latency and backhaul congestion.
Key Benefits of MicroPoPs for ISPs
1. Cost-Effective Network Expansion
Deploying FTTH can be prohibitively expensive in low-density regions. MicroPoPs reduce fiber rollout costs while maintaining ultra-fast speeds by serving multiple customers from a single node.
2. Faster Deployment Times
Unlike full-scale fiber deployments, which require extensive civil work, MicroPoPs can be installed quickly using existing infrastructure, significantly reducing time-to-market.
3. Scalability & Future-Proofing
MicroPoPs allow ISPs to scale their networks incrementally. They can start with targeted deployments in high-demand areas and expand based on user adoption.
4. Improved Service Reliability
By decentralizing data distribution, ISPs can enhance redundancy and reliability, ensuring consistent performance during peak usage.
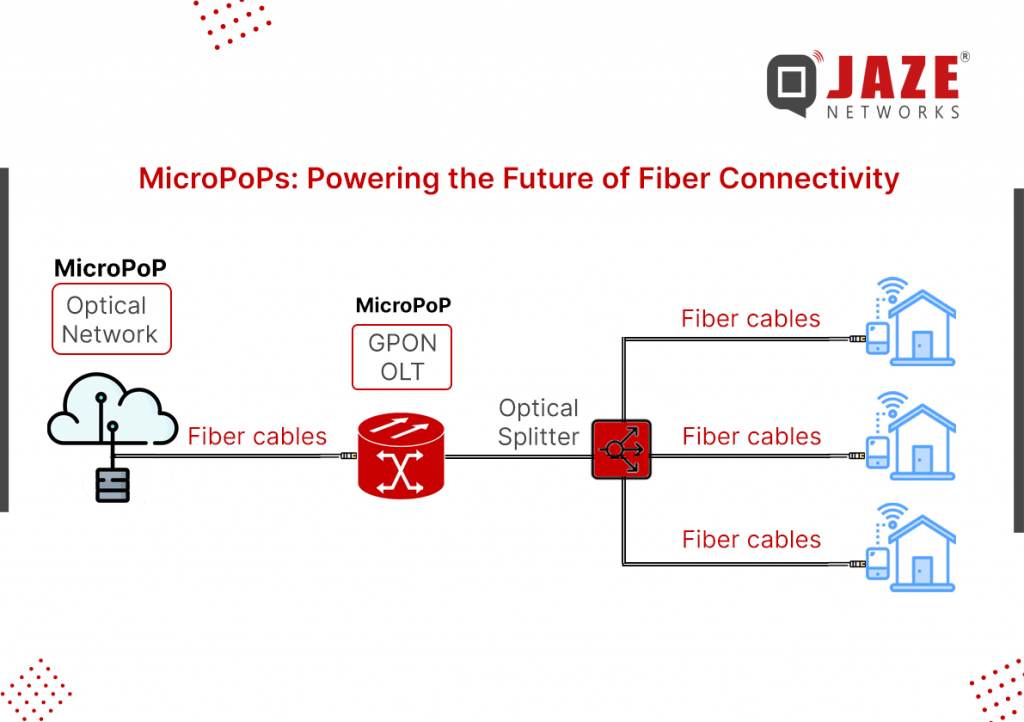
Deployment Considerations for ISPs:
While MicroPoPs offer significant advantages, successful deployment requires careful planning.
Key factors to consider include:
Backhaul Capacity: Ensuring sufficient fiber bandwidth to support high-speed connectivity at each MicroPoP location.
Geographic Placement: Optimal positioning within communities to maximize coverage and minimize last-mile delivery costs.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to local infrastructure and right-of-way regulations.
Power & Cooling: Implementing efficient power and cooling solutions for remote MicroPoP units.
The Future of ISP Networks with MicroPoPs
As ISPs strive to deliver multi-gigabit speeds and support the growing number of connected devices, MicroPoPs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of broadband infrastructure. By integrating next-gen technologies like XGS-PON, 5G backhaul, and edge computing, ISPs can create robust, scalable networks that meet the ever-increasing demands of modern consumers.
MicroPoPs represent a strategic approach to fiber network densification, enabling ISPs to offer high-speed internet with cost efficiency and rapid scalability. By leveraging MicroPoPs, service providers can bridge the digital divide, enhance customer experience, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market.
Deploying and managing MicroPoPs requires a robust and scalable inventory management solution. Jaze ISP Manager simplifies MicroPoP management by keeping track of inventory at each location.
You can also add additional information to subscribers to track which subscriber is connected to which MircoPoP for easier identification and troubleshooting.
In today’s connected world, choosing the right internet service is crucial. With various options available, it can be challenging to determine which one best suits your needs. Two popular choices are fiber and satellite internet. Each has its unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different situations. Let’s dive into the details to help you make an informed decision.
Fibre internet, powered by fiber-optic cables, is known for its exceptional speed and reliability. Here’s a breakdown of its benefits and challenges:
Satellite internet, as the name suggests, relies on satellites to beam internet signals to users on the ground. While it doesn’t match the speed and reliability of fibre, it has its own advantages, especially in remote or underserved areas.
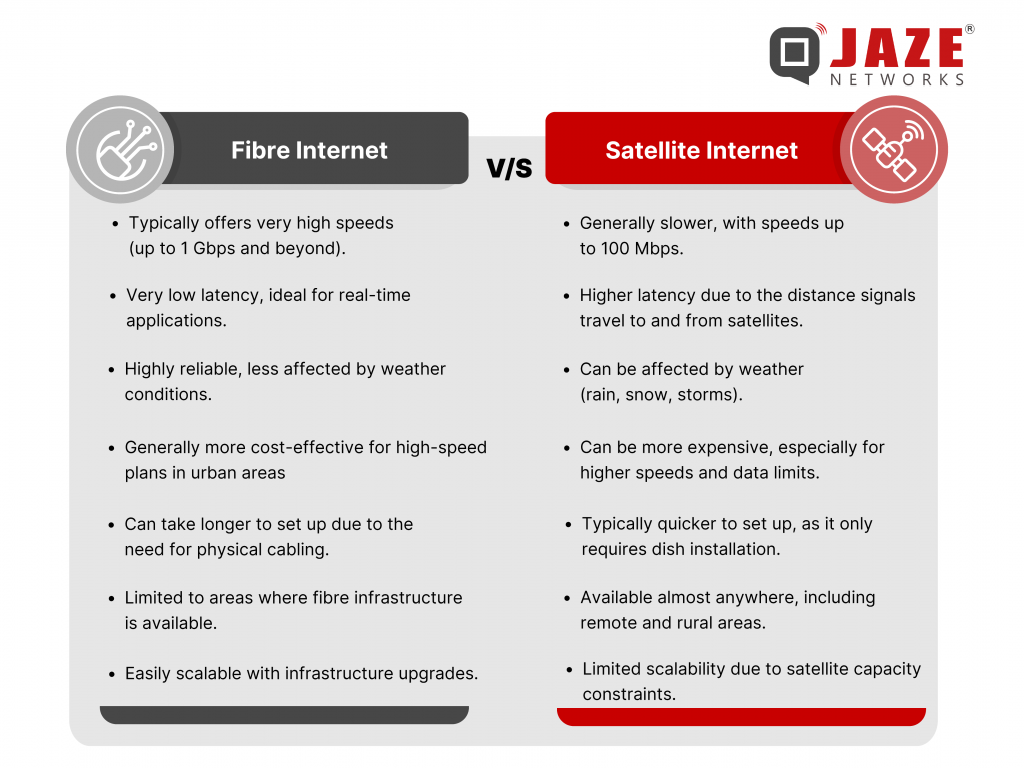
The choice between fibre and satellite internet depends largely on your location, usage needs, and budget.
Despite the growing market of Satellite Internet, fiber based Internet is here to stay. Fiber based ISPs are more reliable with faster speeds and lower latency which provide a better customer experience. ISPs need software to manage their business operations and automate processes.
Jaze ISP Manager integrates with all leading BNG providers to provide scalable and enterprise-grade AAA, BSS and IPDR solutions for ISPs of all sizes. Click here to learn more.
Bandwidth is the amount of data transmitted over a network connection in a given time, measured in bits per second (bps) or megabits per second (Mbps). For streaming, it refers to the data sent and received by your device.
Several factors influence the amount of bandwidth needed for streaming:
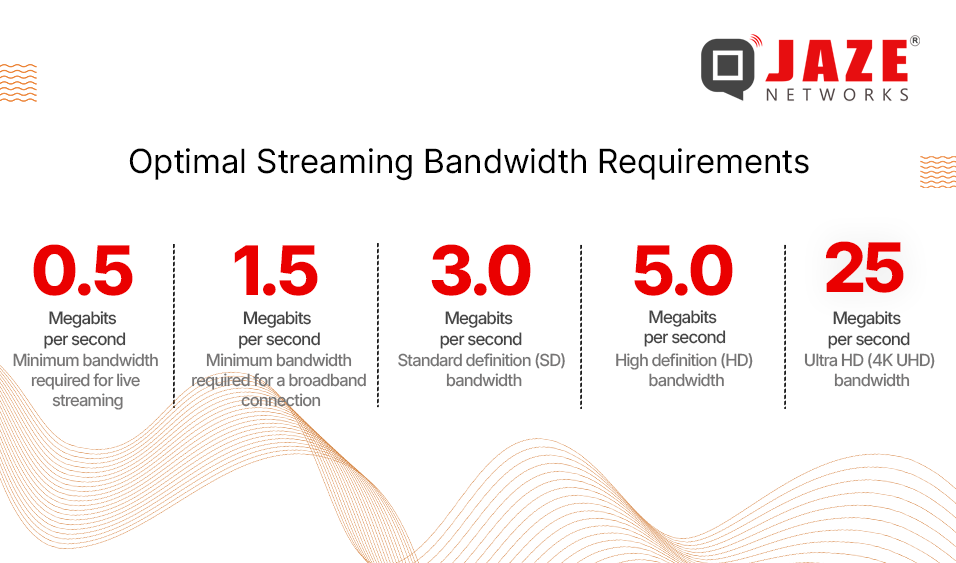
Live streaming requires more bandwidth due to real-time data transmission, while on-demand streaming can buffer content, making it more forgiving on bandwidth. Each streaming platform has its own bandwidth recommendations. For example, YouTube suggests a minimum of 3 Mbps for 720p at 30 fps and 6 Mbps for 1080p at 60 fps. Twitch recommends 3-6 Mbps for most streams.
To calculate your bandwidth needs, use the formula: Bandwidth (Mbps) = Video bitrate (Mbps) + Audio bitrate (Mbps). For instance, 1080p streaming with a 4 Mbps video bitrate and 0.5 Mbps audio bitrate requires 4.5 Mbps total. Add a buffer (25-50%) to account for internet speed fluctuations.
Choosing the Right Codec:
Reducing Video Quality and Frame Rate:
Wired vs. Wireless Connections:
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Bandwidth Issues:
By considering factors like video quality, frame rate, and internet connection, you can estimate your bandwidth needs and make necessary adjustments. Implementing the right strategies will help you enjoy high-quality streams without interruptions.
Jaze ISP Manager provides comprehensive tools for monitoring bandwidth usage, offering real-time insights and detailed usage reports. ISPs can also remotely troubleshoot Wi-Fi issues by gaining insights on connected Wi-Fi devices and signal strength directly from Jaze ISP Manager’s dashboard. Additionally, it allows ISPs to optimize streaming bandwidth by analyzing usage patterns and recommending adjustments to ensure seamless video and audio playback for end-users. Click here for more information.
Launched in 2015, the Digital India Scheme is a transformative initiative by the Indian government aimed at building a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. The program emphasizes three core areas: delivering robust digital infrastructure, offering government services on-demand, and empowering citizens through digital literacy. With high-speed internet as its backbone, the initiative aspires to bridge the digital divide, stimulate innovation, and foster inclusive growth.
The Digital India Scheme revolves around three key areas:
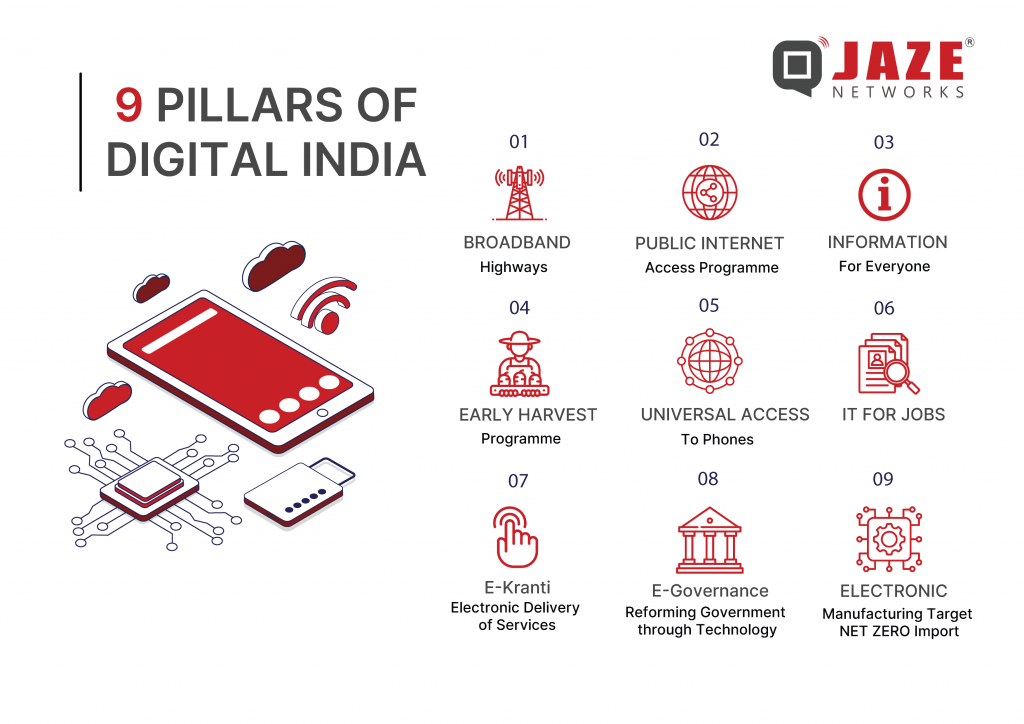
The scheme is built on nine key pillars that drive its mission:
Among these pillars, broadband highways are integral to the program’s success. High-speed internet serves as the backbone for delivering essential services, bridging the urban-rural divide, and fostering economic growth.
The scheme digitizes government services to enhance accessibility. Aadhaar, a unique digital identity, serves as a single authentication point for citizens, streamlining access to various services.
Broadband-enabled CSCs act as hubs for government and private services, including banking, insurance, and digital literacy programs, particularly benefiting rural populations.
With reliable internet connectivity, digital payment systems like Unified Payments Interface (UPI) facilitate secure and efficient transactions, promoting a cashless economy.
Broadband penetration into rural India is one of the most important aspects of the Digital India project which acts as an enabler of other services. The Government of India has deployed a vast network of fiber throughout the country through BHARATNET to connect all Gram Panchayats and villages. Each state has its own special purpose vehicle to make use of the fiber to deliver broadband and other services as part of Digital India.
Broadband delivery requires a complete AAA and BSS solution which integrates with all other components in the network. Jaze ISP Manager delivering an end-to-end solution with comprehensive BSS and AAA solution for broadband delivery across Tamil Nadu through TANFINET. The solution is delivered to be scalable to serve 1 million subscribers delivering high-speed broadband and other services across Tamil Nadu. Click here to learn more.
As of 2023, TRAI has highlighted quality of service (QoS) issues as a persistent concern among Indian consumers, with complaints regarding network disruptions, inconsistent speeds, and hidden fees. TRAI receives thousands of complaints monthly, which indicates widespread dissatisfaction with service quality and transparency in ISP billing practices.
A reliable internet connection is as essential as electricity in today’s digital age. Complaints about poor service quality, hidden charges, and inconsistent speeds are widespread. Understanding if you’re getting your money’s worth from your ISP is crucial. Let’s dive into the ways to determine if your ISP is delivering on its promises.
India’s internet landscape shows a stark contrast in accessibility between urban and rural areas. While urban consumers enjoy more ISP options and higher speeds, rural areas still struggle with connectivity. The rural broadband penetration rate is significantly lower than urban, as per TRAI reports, making it challenging for rural consumers to switch to better providers or find competitive prices. This disparity limits consumer choices and leads to dissatisfaction among rural users, who feel locked into subpar services due to a lack of alternatives.
As India’s internet needs grow, consumers deserve ISPs that provide transparent pricing, reliable speeds, and better access across the country.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs streamline operations with feature-rich and configurable modules including lead management, helpdesk, customer portals and mobile applications in order to help serve customers better. These features ensure reliable service delivery and support to provide a great customer experience. Click here to know more.
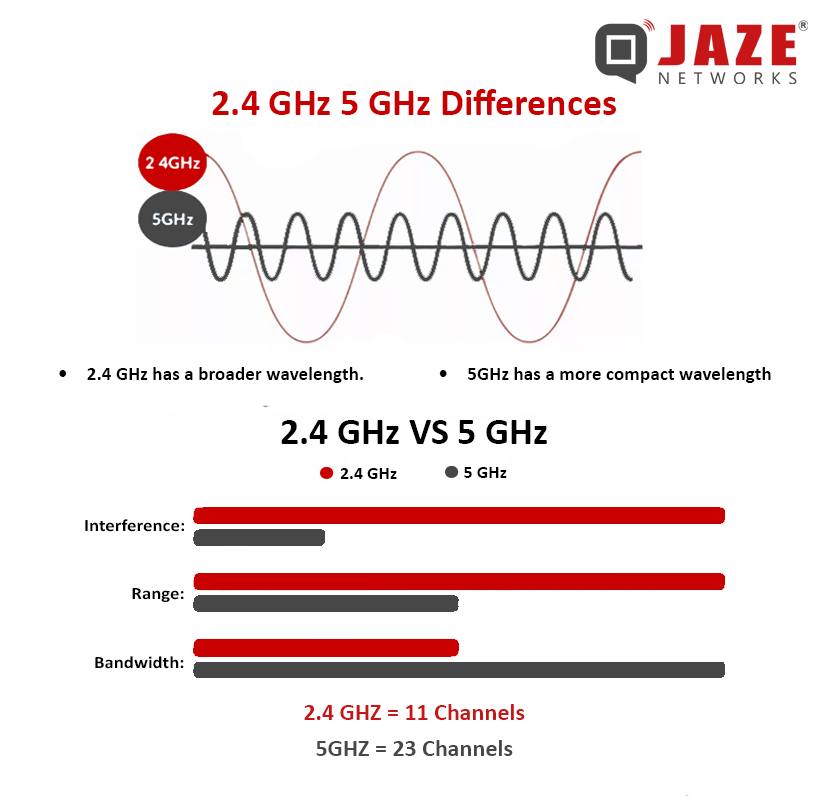
When setting up a Wi-Fi network, you may have noticed two frequency options: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Both frequencies serve the purpose of providing wireless internet, but they operate differently, impacting speed, range, and interference. Let’s break down what each frequency offers to help you choose the best option for your needs.
The numbers 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz refer to radio frequency bands used to transmit data wirelessly. These bands enable devices like smartphones, computers, and smart home devices to communicate with a router, creating a Wi-Fi network. Each frequency has unique characteristics that can influence your connection’s strength and reliability.
The 2.4 GHz band has been around for a while and is often considered the default frequency for most Wi-Fi devices.
Range: One of the main advantages of the 2.4 GHz band is its ability to cover longer distances. The lower frequency waves can penetrate walls and other obstacles more effectively, making it ideal for larger homes or office spaces.
Speed: While the 2.4 GHz band offers decent speeds, it generally maxes out at around 150 Mbps under ideal conditions. This might not be sufficient for data-heavy tasks like streaming HD videos or online gaming.
Interference: This band is more prone to interference because it shares the frequency with many other household devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors. This can lead to slower speeds and dropped connections, especially in densely populated areas.
Compatibility: Most Wi-Fi devices support 2.4 GHz, making it a widely compatible choice.
The 5 GHz band is newer and offers several benefits, particularly in terms of speed and congestion:
Speed: One of the most significant advantages of the 5 GHz band is its ability to support higher data transfer rates. Speeds can reach up to 1,300 Mbps, making it perfect for activities that require a lot of bandwidth, such as streaming HD or 4K videos, online gaming, and large file downloads.
Interference: The 5 GHz band is less crowded compared to the 2.4 GHz band, resulting in less interference from other devices. This can lead to a more stable and faster connection, especially in environments with many Wi-Fi networks.
Range: The higher frequency of the 5 GHz band means it doesn’t cover as much distance as 2.4 GHz and struggles more with obstacles like walls and floors. This can limit its effectiveness in larger spaces or multi-story buildings.
Channels: The 5 GHz band offers more channels, which helps reduce congestion and improve performance in busy environments.
Choosing the right frequency band depends on your specific needs and environment:
2.4 GHz: Ideal for larger homes or offices where coverage over longer distances is crucial. It’s also better for penetrating walls and other obstacles. Use this band if you have older devices that only support 2.4 GHz.
5 GHz: Best for smaller areas or spaces with minimal obstacles where speed is a priority. It’s perfect for high-bandwidth activities like streaming and gaming. Use this band to reduce interference and improve connection stability.
Most modern routers are dual-band, meaning they can broadcast both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz signals simultaneously. This allows you to choose the best band for your needs or even connect different devices to different bands. For example, you could connect your smartphone and smart home devices to the 2.4 GHz band for better range, while using the 5 GHz band for your laptop and gaming console to ensure faster speeds and less interference.
Selecting between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi frequencies can significantly impact network performance, with each band offering unique benefits in range and speed. ISPs will need to choose between single band routers and dual band routers based on the customer’s bandwidth plan and home layout. These will play a crucial role to ensure optimal end user experience. Apart from this ISPs will also need to ensure that these devices are configured as needed and get visibility on devices connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Jaze ISP Manager has built-in ACS with support for TR069 to automatically provision the CPE device along with managing Wi-Fi settings. ISPs can also remotely troubleshoot Wi-Fi issues by gaining insights on connected Wi-Fi devices and signal strength directly from Jaze ISP Manager’s dashboard. Click here for more information. Click here to learn more.