




Real-Time Communications (RTC) — whether video conferencing, live streaming, or VoIP — have become the backbone of modern connectivity. Users expect instant, uninterrupted interaction, and even minor delays can cause frustration. Delivering this level of performance requires more than just fast internet; it relies on understanding Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE), and how they intersect.
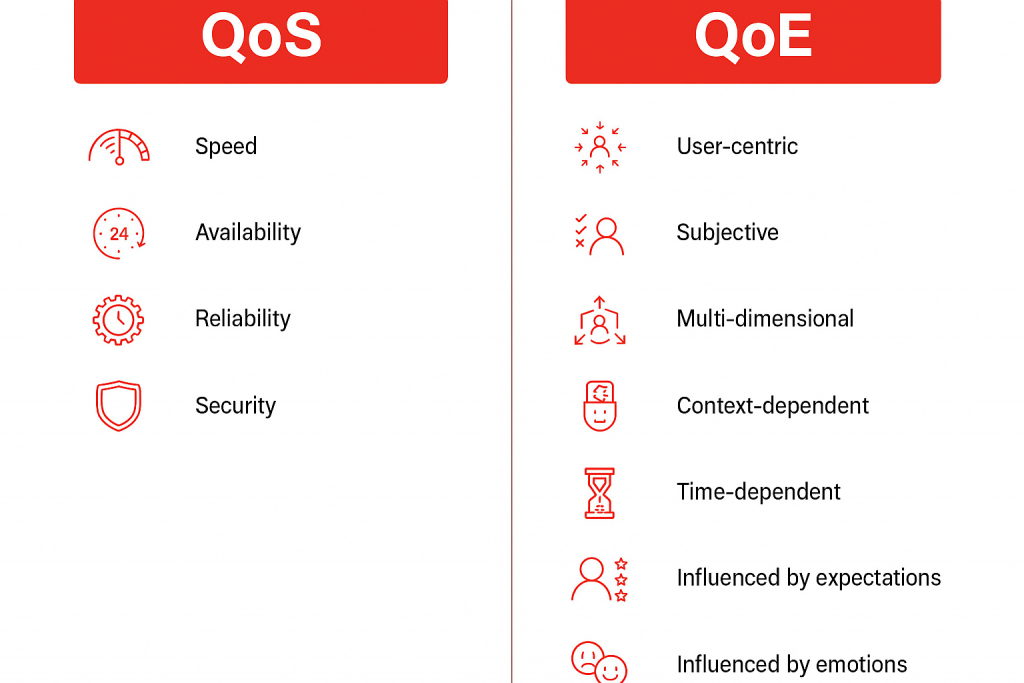
Quality of Service (QoS) is the technical engine that ensures RTC traffic moves efficiently across networks. Without it, calls drop, video lags, and user frustration rises.
Key QoS mechanisms include:
By controlling these network variables, QoS provides measurable reliability — the foundation for any RTC application.
While QoS handles the network, Quality of Experience (QoE) focuses on how users perceive the service. High network performance doesn’t automatically translate into a satisfying experience if the application is difficult to use or inconsistent.
Factors affecting QoE include:
Measuring QoE often involves subjective feedback, such as Mean Opinion Scores (MOS), surveys, or session success rates.
The most successful RTC experiences occur when QoS and QoE are aligned. Network optimizations (QoS) set the stage, but user perception (QoE) determines satisfaction.
For instance, a video conference may have excellent packet delivery, low latency, and zero jitter — but if users struggle to navigate the app or experience confusing error messages, QoE suffers.
Integrated monitoring of both QoS metrics (latency, jitter, packet loss) and QoE indicators (MOS, user engagement) allows providers to proactively identify problems and enhance the overall experience.
Monitoring the right metrics helps bridge technical performance and user satisfaction:
QoS Metrics:
QoE Metrics:
Tracking both sets of metrics ensures service providers can pinpoint issues, whether technical or user-facing.
These strategies provide measurable improvements in both technical performance and user satisfaction.
In a digital-first world, RTC performance can make or break user experiences. QoS ensures the network can deliver real-time data reliably, while QoE measures the perception and satisfaction of the user. Service providers who monitor, optimize, and balance both aspects will not only prevent disruptions but also build trust and loyalty among their users.
Investing in QoS and QoE is not optional — it’s the foundation for RTC success, whether in business, education, or everyday social interactions.
Jaze ISP Manager becomes critical in this equation. In integration with BNG providers, Jaze ISP Manager automates enforcement of intelligent traffic policies, and provides real-time analytics, empowering ISPs to deliver consistent QoS while keeping QoE at the center. The result: seamless RTC experiences, satisfied subscribers, and a future-ready network that scales effortlessly with demand.
Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) is poised to become a game changer. It brings improvements in speed, latency, reliability, and capacity — all critical for modern digital applications. Here’s a clear look at what’s new, why it matters, and what ISPs and network managers should be doing to stay ahead.
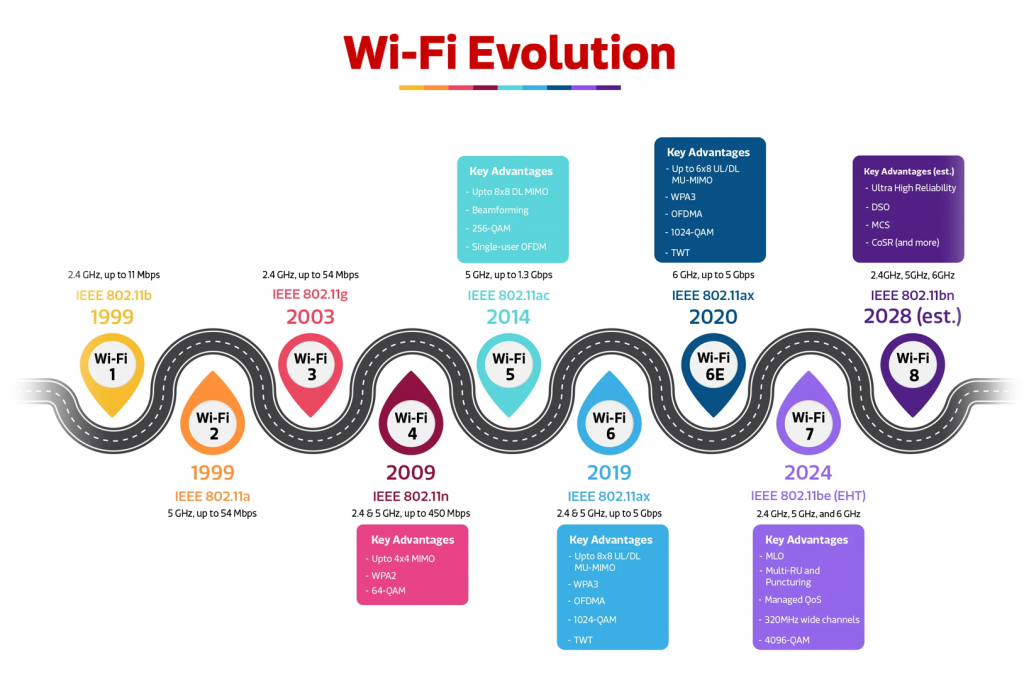
Wi-Fi 7 isn’t just an incremental upgrade — it’s a leap toward connectivity that meets the demands of tomorrow.
Jaze Networks helps businesses and service providers manage users on Wi-Fi networks and deliver seamless Wi-Fi experiences to end-users.
Jaze Access Manager provides solutions in integration with all lead wireless equipment manufacturers to deliver customized on-boarding workflows, granular policies for Wi-Fi Access through AAA and logging for compliance.
Click here to know more on Jaze Access Manager.