




When we talk about internet speed, most people instantly think about how fast they can download movies, stream videos, or browse social media. But in today’s world, it’s not just about downloading anymore — upload speed is equally important.
As we step into 2025–2026, when remote work, cloud storage, video creation, and smart devices dominate daily life, upload speed can make or break your digital experience.
Let’s understand why it matters — and how it affects almost everything you do online.
What Exactly Is Upload Speed?
Upload speed refers to how quickly you can send data from your device to the internet.
It’s measured in megabits per second (Mbps), just like download speed.
Every time you:
—you’re using your upload bandwidth.
If your upload speed is low, even a strong download connection can feel sluggish or unstable during these tasks.
1. The Era of Remote Work & Online Collaboration
Work-from-home and hybrid models are here to stay. Every video meeting, shared file, or cloud document relies on your upload connection.
A slow upload speed means blurry video calls, lagging audio, and constant “reconnecting…” messages — not ideal when you’re presenting to clients or attending classes online.
2. Social Media & Content Creation Boom
From influencers to small business owners, everyone is uploading photos, reels, and videos daily.
With 4K and 8K becoming standard, files are huge. High upload speed ensures your videos go live faster — and without frustrating delays.
3. Cloud Storage & Backup
We’re moving away from storing everything on devices. Automatic backups to Google Photos, iCloud, and OneDrive constantly use upload bandwidth.
If upload speeds are low, backups slow down, sync fails, and your data may remain outdated.
4. Smart Homes & IoT Devices
Cameras, sensors, and voice assistants send continuous data to cloud servers.
When upload bandwidth is insufficient, you’ll see camera feed delays, failed device syncs, or unreliable smart automation.
5. Gaming & Live Streaming
Gamers know the pain of lag.Online gaming and live streaming both rely on strong upstream connections — every action, every frame, every voice chat goes out through your upload channel.
Higher upload speeds mean smoother gameplay and crystal-clear streams.
| Online Activity | Recommended Upload Speed |
| Video calls (Zoom, Meet) | 3–5 Mbps |
| Cloud backups | 10–20 Mbps |
| Online gaming | 5–10 Mbps |
| 4K live streaming | 20–25 Mbps |
| Uploading large media files | 25 Mbps and above |
If multiple devices or users share the same connection, you’ll need even higher speeds for a seamless experience.

India’s internet usage pattern is shifting fast. Earlier, most users were consumers of content — watching, downloading, or streaming.
But now, millions are creators — students uploading projects, professionals hosting webinars, and entrepreneurs managing online stores.
Unfortunately, many broadband plans in India still prioritize download speeds and offer much lower uploads (often just 10–20% of download rates).
That imbalance is slowly changing, as fiber networks and symmetrical connections become mainstream.
Traditional broadband (like copper or DSL) can’t handle equal upload and download speeds.
But fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) connections deliver symmetrical speeds — meaning if you get 200 Mbps download, you also get 200 Mbps upload.
This makes a huge difference for:
Fiber technology is the backbone of India’s digital growth — and it’s finally bridging the upload gap.
As India embraces a creator-driven digital economy, upload speed is no longer secondary — it’s essential.
Whether you’re working from home, managing an online business, or sharing your creativity with the world, faster upload speeds ensure smoother, smarter, and more reliable connectivity.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs by optimising bandwidth delivery and provide a seamless experience to subscribers. This ensures stable upload speeds for users, reduces congestion during peak hours, and improves performance for video calls, cloud backups, and live streaming. In short, it gives ISPs the tools to maintain reliable upstream performance for their customers. Click here to know more
Remember the days when every device needed a wire? A mess of Ethernet cables under your desk, behind your TV, and snaking across the living room? That’s about to become history.
Wi-Fi 7 is not just another upgrade in wireless technology — it’s a leap into the future. With unprecedented speeds, lower latency, and smarter connections, it’s designed to replace the Ethernet cable for most users. Let’s dive into why it’s time to cut the cord.
Speed
Latency
Capacity
Bandwidth
Efficiency
For years, Ethernet has been the go-to for speed and stability. But Wi-Fi 7 changes the game:
Wi-Fi 7 routers are starting to roll out, bringing enterprise-grade wireless capabilities to homes and businesses. If you’re setting up a new workspace or upgrading your network, this is the tech to watch.
Say goodbye to tangled cables, drilling holes in walls, and limited mobility. Wi-Fi 7 is here — and the future is wireless.
Wi-Fi 7 brings the next leap in wireless connectivity—offering ultra-fast speeds, significantly lower latency, and higher efficiency for high-density environments. With support for demanding applications like 8K streaming, AR/VR, and real-time collaboration, Wi-Fi 7 is built to meet the needs of modern, high-performance networks.
Jaze Access Manager seamlessly integrates with all leading Wi-Fi 7 vendors, delivering fully managed hotspots and 802.1x authentication through RADIUS-based AAA, ideal for secure guest access and scalable campus wireless deployments. Click here to know more
Wi-Fi 7 represents a significant leap forward in wireless networking, offering unparalleled speed, efficiency, and capacity. Its advanced features are set to transform the way we experience connectivity in both home and office environments. Ensuring that networks are equipped to handle the demands of today’s digital world and beyond.
Building upon the foundation of its predecessors, Wi-Fi 7 introduces a suite of enhancements designed to meet the burgeoning needs of modern applications.
Wi-Fi 7, officially known as IEEE 802.11be, is the newest standard in wireless networking. While maintaining backward compatibility with previous Wi-Fi versions, it offers significant improvements in speed, efficiency, and capacity.
While Wi-Fi 7 is backward compatible with earlier Wi-Fi standards, unlocking its full potential requires upgrading to Wi-Fi 7-enabled devices and routers. Early adopters can expect to see routers and access points from major manufacturers becoming available, with devices like smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs following suit. As the technology matures, a broader range of Wi-Fi 7-compatible products will enter the market, making it an opportune time to consider future-proofing your home or office network.
Jaze Access Manager integrates with all leading Wi-Fi 7 vendors to provide managed hotspots and 802.1x authentication with radius based AAA for guest access and campus wireless networks. Click here to know more
Bandwidth is the amount of data transmitted over a network connection in a given time, measured in bits per second (bps) or megabits per second (Mbps). For streaming, it refers to the data sent and received by your device.
Several factors influence the amount of bandwidth needed for streaming:
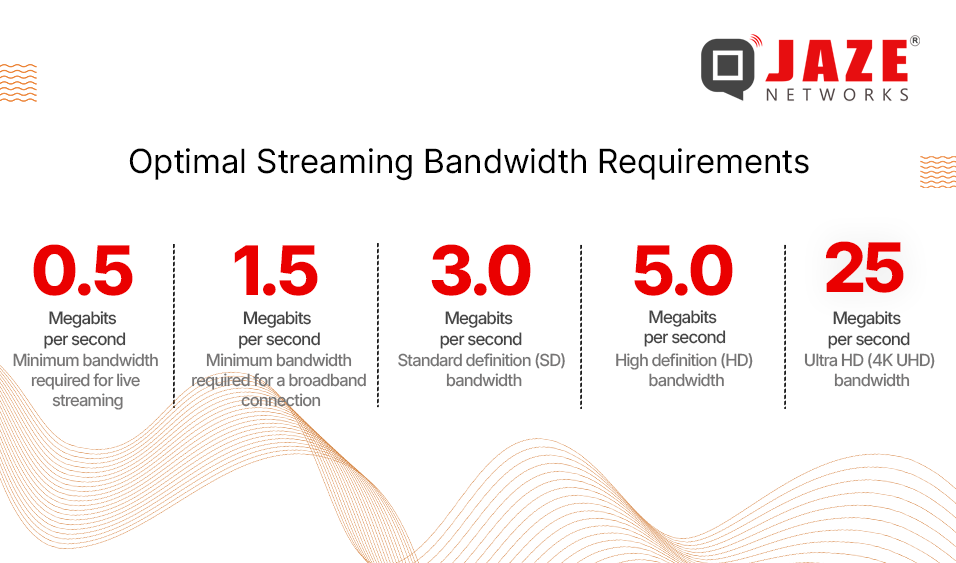
Live streaming requires more bandwidth due to real-time data transmission, while on-demand streaming can buffer content, making it more forgiving on bandwidth. Each streaming platform has its own bandwidth recommendations. For example, YouTube suggests a minimum of 3 Mbps for 720p at 30 fps and 6 Mbps for 1080p at 60 fps. Twitch recommends 3-6 Mbps for most streams.
To calculate your bandwidth needs, use the formula: Bandwidth (Mbps) = Video bitrate (Mbps) + Audio bitrate (Mbps). For instance, 1080p streaming with a 4 Mbps video bitrate and 0.5 Mbps audio bitrate requires 4.5 Mbps total. Add a buffer (25-50%) to account for internet speed fluctuations.
Choosing the Right Codec:
Reducing Video Quality and Frame Rate:
Wired vs. Wireless Connections:
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Bandwidth Issues:
By considering factors like video quality, frame rate, and internet connection, you can estimate your bandwidth needs and make necessary adjustments. Implementing the right strategies will help you enjoy high-quality streams without interruptions.
Jaze ISP Manager provides comprehensive tools for monitoring bandwidth usage, offering real-time insights and detailed usage reports. ISPs can also remotely troubleshoot Wi-Fi issues by gaining insights on connected Wi-Fi devices and signal strength directly from Jaze ISP Manager’s dashboard. Additionally, it allows ISPs to optimize streaming bandwidth by analyzing usage patterns and recommending adjustments to ensure seamless video and audio playback for end-users. Click here for more information.
The landscape of entertainment consumption has dramatically transformed with the rise of video streaming, marking a significant shift from traditional broadcast TV to internet-based services.
As video streaming becomes increasingly popular, two key technologies have emerged: IPTV and OTT services.
According to recent data from Statista, the OTT video market is anticipated to reach approximately 6.4 billion users by 2029. Meanwhile, the global IPTV market was valued at USD 59.68 billion in 2022. But what are IPTV and OTT, and how do they differ?
Network Type: IPTV operates on a closed, managed network provided by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). This ensures a controlled environment for content delivery, leading to more stable and reliable streams.
OTT services utilize the open, public internet, making them accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Monetization Models: IPTV services are typically subscription-based and often bundled with other internet services provided by ISPs.
OTT services offer more flexible monetization options, including both subscription-based and ad-supported models. This variety allows OTT platforms to cater to different user preferences and budgets, providing more accessibility and choice.
Content Quality: IPTV is known for delivering high-quality, reliable streams due to its controlled network conditions. The managed network minimizes buffering and interruptions, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
OTT content quality, however, can vary significantly based on the viewer’s internet speed and network congestion.
Accessibility: IPTV services are limited to the service provider’s network, often making them region-specific. This means that users can only access IPTV content within the geographical area covered by their ISP.
OTT services are globally accessible as long as there is an internet connection. This global reach allows users to access content from anywhere in the world, making OTT a more versatile option for international viewers.
Equipment: To access IPTV services, users typically need a set-top box and sometimes additional hardware. This equipment is necessary to decode the IPTV signal and deliver it to the TV.
OTT services are accessible on a wide range of devices without the need for special equipment. Users can stream OTT content on smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers, providing greater convenience and flexibility.
Operational Costs: IPTV services incur higher operational costs due to the need for dedicated infrastructure and equipment. These costs are often passed on to consumers through higher subscription fees.
OTT services leverage existing internet infrastructure, resulting in lower operational costs.
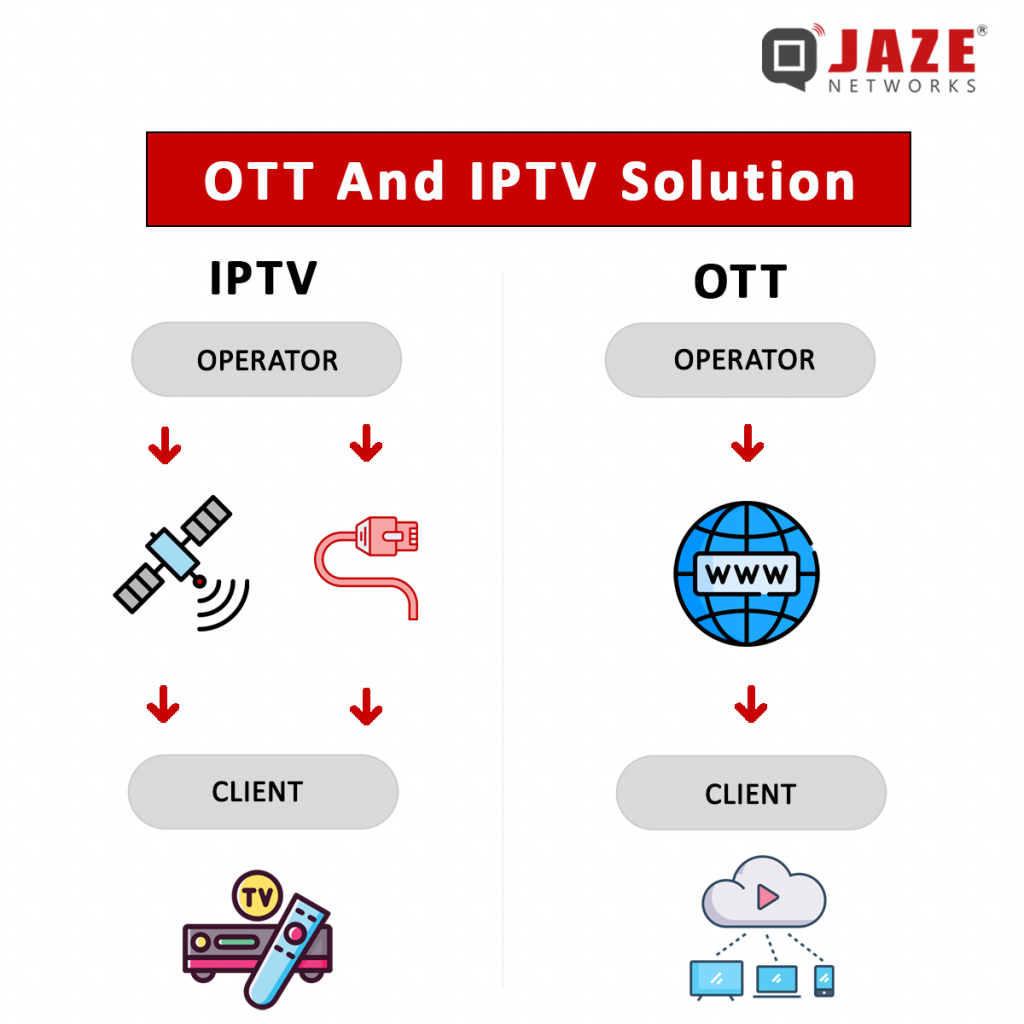
IPTV, or Internet Protocol Television, delivers television content through a private, managed network. This means that the service provider controls the entire delivery process, ensuring a high-quality, reliable viewing experience. IPTV typically requires a subscription and a set-top box to decode the signal and deliver it to your TV.
Once the setup is complete, users can enjoy a wide range of TV programming over their internet connection. In essence, IPTV represents a shift towards a more flexible and efficient television experience, offering on-demand access to a diverse array of programming through a managed network.
OTT, or Over-The-Top, refers to content delivered over the public internet. Unlike IPTV, OTT does not require a managed network or a set-top box. Instead, it can be accessed on a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers. Popular OTT services include Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video.
While both IPTV and OTT offer unique advantages, OTT services have become the preferred choice for many consumers and providers. The flexibility and lower cost of OTT platforms make them more appealing, especially in today’s mobile-first world where users value the ability to watch content on-the-go.
OTT services also stand out for their user-friendly nature. There’s no need for specialized equipment or installation—just an internet connection and a device. This ease of use, combined with a vast library of on-demand content, has contributed to the widespread adoption of OTT over IPTV.
Choosing between IPTV and OTT depends on your specific needs and preferences. IPTV might be ideal for those seeking high-quality, live streaming within a controlled network, especially for events like sports. However, for most users, OTT offers a more versatile and cost-effective solution, allowing access to a broad array of content across multiple devices.
With ISPs offering multiple services, managing billing and services for OTT and IPTV can be challenging. Jaze ISP Manager simplifies this process by integrating with top OTT and IPTV platforms and aggregators. It automates billing and efficiently manages OTT and IPTV services, including activation and deactivation. Additionally, Jaze ISP Manager integrates with leading BNG providers to help deliver differentiated policies, enhancing the Quality of Experience for the ISP’s subscribers. Click here to learn more.