




In an era where streaming, video conferencing, and real-time gaming dominate digital activity, most users still equate better internet with higher bandwidth. But the real indicators of network quality lie deeper—in factors like latency, jitter, and bufferbloat. Understanding these metrics is essential to achieving consistent, high-quality connectivity.
While bandwidth defines the maximum data transfer capacity, it doesn’t ensure consistent delivery. Think of bandwidth as the width of a pipe, not the speed or smoothness of water flow. High bandwidth with unmanaged latency and jitter can still lead to poor Quality of Experience (QoE).
Latency measures the round-trip time data takes to travel between a device and a server. High latency creates noticeable delays, especially during:
Solution:
Jitter represents fluctuations in packet arrival times, which leads to data arriving out of sync. This is particularly disruptive for time-sensitive applications like:
Solution:
Bufferbloat occurs when network devices over-buffer packets, introducing delay and congestion even when bandwidth is not fully utilized.
Symptoms include:
Solution:
While a fast connection helps with large file downloads or 4K streaming, real-time communication depends more on network consistency than on raw speed.
Best Practices:
For ISPs and enterprise network managers, focusing solely on delivering higher speeds is no longer sufficient. Real competitive advantage lies in offering:
Maximizing internet performance isn’t about bandwidth alone. To truly optimize the end-user experience, network administrators and users alike must address the hidden factors—latency, jitter, and bufferbloat—that directly influence application responsiveness and reliability.
Investing in smarter infrastructure, performance-aware configurations, and end-to-end visibility will ultimately provide a smoother, faster, and more predictable network experience for all users.
To improve Quality of Experience (QoE) beyond just bandwidth, Jaze ISP Manager equips ISPs with meaningful insights into subscriber usage.
Jaze ISP manager in integration with BNG routers supporting FQ-CODEL based AQM helps to optimize the quality of experience effectively managing latency, jitter, and bufferbloat.
Click here to know more.
A slow internet connection can be more than just frustrating—it can disrupt work, entertainment, and everyday online activities. Understanding the reasons behind this slowdown and knowing how to fix it can help you get back to enjoying a seamless online experience.
Here are five common reasons why your internet might be slowing down and how you can address them.
Where your router is placed can have a significant impact on the strength and reach of your Wi-Fi signal. If your router is hidden in a closet, placed in a basement, or tucked behind furniture, it’s likely struggling to transmit a strong signal across your home.
Open spaces work best for routers as they minimize obstructions. If your house is large or has multiple floors, consider investing in a mesh Wi-Fi system or a range extender to ensure seamless connectivity in all areas.
The increasing number of connected devices in homes today can overload your network. From smartphones and laptops to smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices, each connection uses bandwidth. The more devices connected, the slower the speeds for everyone.
Start by identifying devices that don’t need constant internet access and disconnect them. Many modern routers come with Quality of Service (QoS) settings, allowing you to prioritize bandwidth for critical activities such as video calls or gaming. If you frequently face bandwidth issues, consider upgrading to a higher-speed internet plan that can handle multiple devices simultaneously.
Technology evolves quickly, and older routers or devices may not support current Wi-Fi standards. These outdated devices can bottleneck your internet speed, even if your ISP provides high-speed service.
Ensure your router supports modern Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), which offer faster speeds and better handling of multiple devices. Don’t forget to check for firmware updates for your router, as they can improve performance and security.
Wi-Fi signals operate on specific channels, and if your neighbors’ networks use the same channels, interference can slow down your connection. This issue is particularly common in densely populated areas or apartment complexes.
Most modern routers have an option to automatically select the least congested channel. If this feature isn’t available, use tools like a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify less crowded channels and manually switch your router to one of those. Additionally, placing your router further away from your neighbors’ Wi-Fi sources can reduce interference.
Over time, routers accumulate temporary data that can clog up their system and slow down your connection. A simple reboot can often resolve these minor glitches and restore optimal performance.
Make it a habit to reboot your router at least once a week. Unplug it, wait 30 seconds, and then plug it back in. This clears the router’s memory and refreshes the connection. While rebooting, check for any available firmware updates to ensure your router is running the latest software.
Additional Tips for Improving Internet Speed
Jaze ISP Manager provides built-in integration with broadband routers and CPE devices to monitor Tx/RX levels and Wi-Fi parameters through TR-069 directly from the dashboard. This helps to troubleshoot Wi-Fi signal issues and monitor network performance of end-user devices. Click here to learn more.
Launched in 2015, the Digital India Scheme is a transformative initiative by the Indian government aimed at building a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. The program emphasizes three core areas: delivering robust digital infrastructure, offering government services on-demand, and empowering citizens through digital literacy. With high-speed internet as its backbone, the initiative aspires to bridge the digital divide, stimulate innovation, and foster inclusive growth.
The Digital India Scheme revolves around three key areas:
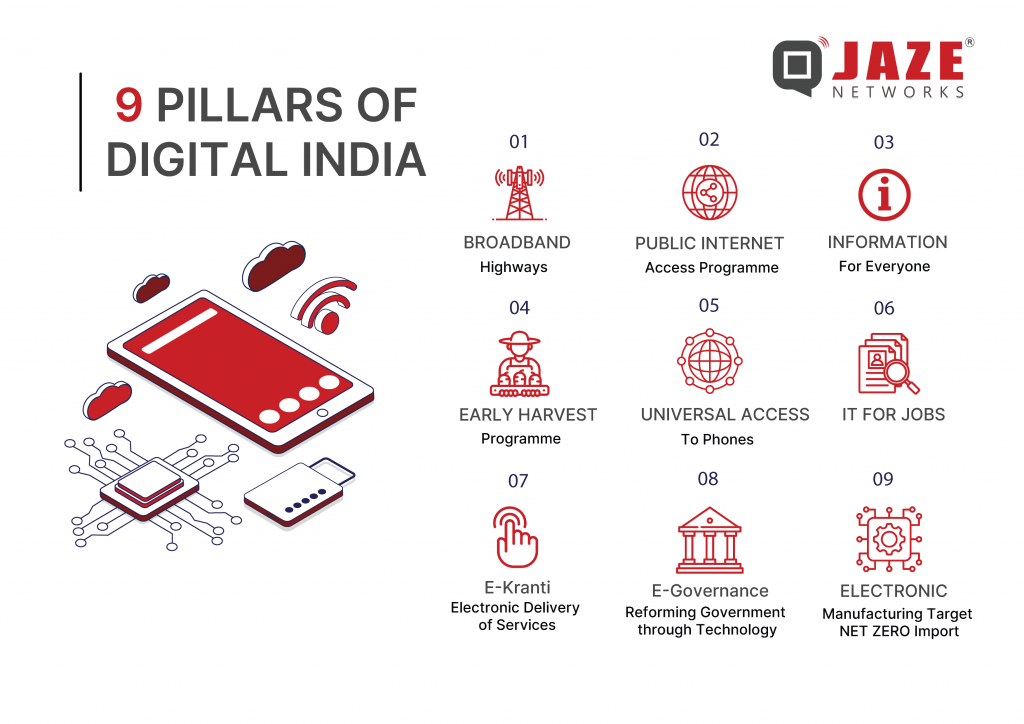
The scheme is built on nine key pillars that drive its mission:
Among these pillars, broadband highways are integral to the program’s success. High-speed internet serves as the backbone for delivering essential services, bridging the urban-rural divide, and fostering economic growth.
The scheme digitizes government services to enhance accessibility. Aadhaar, a unique digital identity, serves as a single authentication point for citizens, streamlining access to various services.
Broadband-enabled CSCs act as hubs for government and private services, including banking, insurance, and digital literacy programs, particularly benefiting rural populations.
With reliable internet connectivity, digital payment systems like Unified Payments Interface (UPI) facilitate secure and efficient transactions, promoting a cashless economy.
Broadband penetration into rural India is one of the most important aspects of the Digital India project which acts as an enabler of other services. The Government of India has deployed a vast network of fiber throughout the country through BHARATNET to connect all Gram Panchayats and villages. Each state has its own special purpose vehicle to make use of the fiber to deliver broadband and other services as part of Digital India.
Broadband delivery requires a complete AAA and BSS solution which integrates with all other components in the network. Jaze ISP Manager delivering an end-to-end solution with comprehensive BSS and AAA solution for broadband delivery across Tamil Nadu through TANFINET. The solution is delivered to be scalable to serve 1 million subscribers delivering high-speed broadband and other services across Tamil Nadu. Click here to learn more.
As of 2023, TRAI has highlighted quality of service (QoS) issues as a persistent concern among Indian consumers, with complaints regarding network disruptions, inconsistent speeds, and hidden fees. TRAI receives thousands of complaints monthly, which indicates widespread dissatisfaction with service quality and transparency in ISP billing practices.
A reliable internet connection is as essential as electricity in today’s digital age. Complaints about poor service quality, hidden charges, and inconsistent speeds are widespread. Understanding if you’re getting your money’s worth from your ISP is crucial. Let’s dive into the ways to determine if your ISP is delivering on its promises.
India’s internet landscape shows a stark contrast in accessibility between urban and rural areas. While urban consumers enjoy more ISP options and higher speeds, rural areas still struggle with connectivity. The rural broadband penetration rate is significantly lower than urban, as per TRAI reports, making it challenging for rural consumers to switch to better providers or find competitive prices. This disparity limits consumer choices and leads to dissatisfaction among rural users, who feel locked into subpar services due to a lack of alternatives.
As India’s internet needs grow, consumers deserve ISPs that provide transparent pricing, reliable speeds, and better access across the country.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs streamline operations with feature-rich and configurable modules including lead management, helpdesk, customer portals and mobile applications in order to help serve customers better. These features ensure reliable service delivery and support to provide a great customer experience. Click here to know more.
When setting up a Wi-Fi network, you may have noticed two frequency options: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Both frequencies serve the purpose of providing wireless internet, but they operate differently, impacting speed, range, and interference. Let’s break down what each frequency offers to help you choose the best option for your needs.
The numbers 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz refer to radio frequency bands used to transmit data wirelessly. These bands enable devices like smartphones, computers, and smart home devices to communicate with a router, creating a Wi-Fi network. Each frequency has unique characteristics that can influence your connection’s strength and reliability.
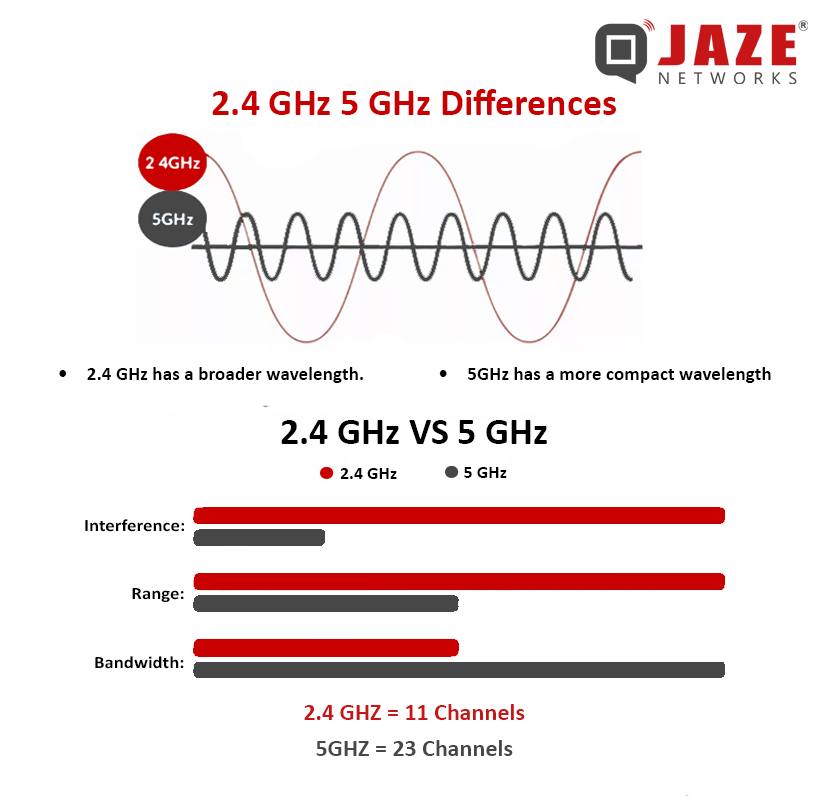
The 2.4 GHz band has been around for a while and is often considered the default frequency for most Wi-Fi devices.
Range: One of the main advantages of the 2.4 GHz band is its ability to cover longer distances. The lower frequency waves can penetrate walls and other obstacles more effectively, making it ideal for larger homes or office spaces.
Speed: While the 2.4 GHz band offers decent speeds, it generally maxes out at around 150 Mbps under ideal conditions. This might not be sufficient for data-heavy tasks like streaming HD videos or online gaming.
Interference: This band is more prone to interference because it shares the frequency with many other household devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors. This can lead to slower speeds and dropped connections, especially in densely populated areas.
Compatibility: Most Wi-Fi devices support 2.4 GHz, making it a widely compatible choice.
The 5 GHz band is newer and offers several benefits, particularly in terms of speed and congestion:
Speed: One of the most significant advantages of the 5 GHz band is its ability to support higher data transfer rates. Speeds can reach up to 1,300 Mbps, making it perfect for activities that require a lot of bandwidth, such as streaming HD or 4K videos, online gaming, and large file downloads.
Interference: The 5 GHz band is less crowded compared to the 2.4 GHz band, resulting in less interference from other devices. This can lead to a more stable and faster connection, especially in environments with many Wi-Fi networks.
Range: The higher frequency of the 5 GHz band means it doesn’t cover as much distance as 2.4 GHz and struggles more with obstacles like walls and floors. This can limit its effectiveness in larger spaces or multi-story buildings.
Channels: The 5 GHz band offers more channels, which helps reduce congestion and improve performance in busy environments.
Choosing the right frequency band depends on your specific needs and environment:
2.4 GHz: Ideal for larger homes or offices where coverage over longer distances is crucial. It’s also better for penetrating walls and other obstacles. Use this band if you have older devices that only support 2.4 GHz.
5 GHz: Best for smaller areas or spaces with minimal obstacles where speed is a priority. It’s perfect for high-bandwidth activities like streaming and gaming. Use this band to reduce interference and improve connection stability.
Most modern routers are dual-band, meaning they can broadcast both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz signals simultaneously. This allows you to choose the best band for your needs or even connect different devices to different bands. For example, you could connect your smartphone and smart home devices to the 2.4 GHz band for better range, while using the 5 GHz band for your laptop and gaming console to ensure faster speeds and less interference.
Selecting between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi frequencies can significantly impact network performance, with each band offering unique benefits in range and speed. ISPs will need to choose between single band routers and dual band routers based on the customer’s bandwidth plan and home layout. These will play a crucial role to ensure optimal end user experience. Apart from this ISPs will also need to ensure that these devices are configured as needed and get visibility on devices connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Jaze ISP Manager has built-in ACS with support for TR069 to automatically provision the CPE device along with managing Wi-Fi settings. ISPs can also remotely troubleshoot Wi-Fi issues by gaining insights on connected Wi-Fi devices and signal strength directly from Jaze ISP Manager’s dashboard. Click here for more information. Click here to learn more.
Video codecs are essential in determining video quality, file size, and playback performance. H.264 and H.265 are two popular codecs, each offering unique benefits. Let’s explore their differences to help you choose the right one for your needs.
H.264, also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), is a widely adopted video compression standard used in a variety of applications, including streaming services, Blu-ray discs, and online platforms like YouTube. Its broad compatibility and efficiency have made it a favorite in the industry.
Key Features:
Compatibility: Supported across nearly all devices and platforms.
Compression Efficiency: Offers moderate compression with good video quality but produces larger file sizes compared to more recent codecs.
Lower Processing Power: Ideal for use on older devices due to its lower computing power requirements.
H.265, or High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is the successor to H.264, developed to provide better compression while maintaining high video quality. It excels at high-resolution formats, like 4K and 8K, and significantly reduces file sizes without compromising visual quality.
Key Features:
Better Compression: Reduces file size by about 50% compared to H.264.
High-Resolution Support: Supports up to 8K resolution, making it suitable for modern content.
Adaptive Streaming: Ideal for smoother streaming at varying bandwidths.

H.265’s major advantage is its ability to maintain the same video quality as H.264 but at half the bitrate, which leads to significantly smaller file sizes. This is beneficial for streaming, storage, and reducing bandwidth usage.
| Feature | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) |
| Compression Efficiency | Good | Excellent |
| Compatibility | Very High | Moderate |
| Video Quality | High | Higher |
| Processing Power | Lower | Higher |
| Use Case | General use, live streaming, video conferencing | High-resolution content, storage-limited scenarios |
| Resolution | H.264/AVC Bandwidth Required | H.265/HEVC Bandwidth Required |
| 480p | 1.5 Mbps | 0.75 Mbps |
| 720p | 3 Mbps | 1.5 Mbps |
| 1080p | 6 Mbps | 3 Mbps |
| 4K | 32 Mbps | 15 Mbps |
Although H.265 offers superior compression, it requires more processing power for both encoding and decoding. This means that older devices might struggle to play H.265 videos unless they have dedicated hardware support for HEVC.
H.264: Works seamlessly on most older and modern devices.
H.265: May require newer hardware and HEVC support for smooth playback.
Use Cases
H.264: Ideal for live streaming, video conferencing, and platforms that require broad compatibility. It’s the go-to codec for general use and applications where reliability and universal support are crucial.
H.265: Best suited for applications requiring high-resolution video, such as 4K and 8K streaming, and situations where storage space is limited. H.265 is also a good choice for future-proofing content as more devices begin to support this codec.
Many modern platforms now support H.265/HEVC due to its enhanced efficiency for high-quality streaming. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that allow H.265/HEVC ingestion from third-party encoders, include:
For ISPs seeking to optimize bandwidth delivery, Jaze ISP Manager seamlessly integrates with top BNG providers supporting both RADIUS and Diameter protocols for flexible policy delivery and ensuring a seamless end user experience. Click here for more information.
As the landscape of home entertainment evolves, the competition between IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) and traditional cable TV intensifies. With the growing trend of cord-cutting, viewers face a pivotal decision about which option aligns best with their viewing preferences and lifestyle. This guide examines the essential differences between IPTV and cable TV, empowering you to make an informed choice about your entertainment future.

Cable TV: The Traditional Approach
Cable TV has long been the dominant method for delivering television content. It relies on coaxial cables to transmit signals to your TV. This well-established technology provides some clear benefits:
Stability: Cable TV is reliable and less dependent on external factors like internet speed.
Quality: Picture and sound quality remain consistent without buffering issues.
However, cable TV does come with its limitations. It is geographically bound, meaning you need access to the provider’s physical network, and the channel selection is often bundled into large packages, which may include unwanted content.
IPTV: The Internet Revolution
IPTV is a modern alternative, utilizing your internet connection to stream content. It offers significant flexibility in terms of device compatibility, letting you watch on your TV, smartphone, or tablet. With IPTV, users enjoy:
Customization: Pick the channels or programs that interest you, instead of settling for bundled packages.
Global Access: View content from around the world, bypassing geographic limitations.
Cable TV: Bundled Services and Contracts
Cable TV providers often offer bundled services that include internet and phone packages. While this might seem cost-effective at first glance, hidden fees for equipment rentals or installation, along with long-term contracts, can make it more expensive in the long run.
IPTV: Flexible and Transparent Pricing
IPTV services usually have straightforward pricing models. With subscription-based plans, you can pay for just the content you want, without any long-term commitment. Additionally, there are no equipment rentals or hefty installation fees, which makes IPTV an attractive option for those seeking flexibility in budgeting.
Cable TV: Familiar Offerings
Cable TV provides access to a wide range of channels, including local programming and live sports. However, its content library is often restricted to what the provider offers within its region, limiting options for international or niche programming.
IPTV: A World of Content
One of IPTV’s major advantages is its vast library of on-demand content, spanning across different genres, languages, and countries. IPTV platforms allow you to explore international programming and tailor your viewing experience based on specific interests, whether it’s niche content or blockbuster movies.
Cable TV: Traditional Navigation
Cable TV interfaces are generally simple but dated. Users navigate through a traditional TV guide, and DVR options allow for recording shows. However, searching for specific content can be slow, and the interface is not designed for personalized recommendations.
IPTV: Modern and Intuitive
IPTV services often provide more user-friendly platforms. You can search for content quickly, receive personalized recommendations based on viewing history, and synchronize your watching experience across multiple devices. This modern convenience is a big win for users who want an effortless interface.
Cable TV: Consistent Performance
Cable TV offers stable picture quality, with many channels available in high definition (HD). However, 4K content is still rare in traditional cable packages, limiting options for viewers with ultra-high-definition TVs.
IPTV: Leading the Quality Race
IPTV is more advanced when it comes to high-quality content. Many services provide access to 4K resolution and HDR (High Dynamic Range) content. Additionally, IPTV platforms use adaptive streaming, adjusting picture quality based on your internet speed, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
Cable TV: Stability Under All Conditions
One of the major advantages of cable TV is its reliability. It remains unaffected by internet outages, and performance is generally consistent. It’s less susceptible to external factors like weather, making it a dependable choice.
IPTV: Dependent on Internet Connectivity
IPTV services, however, depend entirely on your internet connection. This means that buffering, reduced quality, or even service interruptions can occur during periods of slow or unstable internet. High-speed broadband is essential to ensure a smooth viewing experience.
Cable TV: Regulated and Secure
Cable TV is governed by strict regulations, ensuring all content is licensed and distributed legally. There’s also less concern over data collection, as cable TV providers don’t typically track or sell your viewing data.
IPTV: A Mixed Legal Landscape
While many IPTV providers operate legally, some services can fall into legal gray areas, particularly if they offer content without proper licensing. Users should be cautious and opt for reputable IPTV providers that comply with local regulations. Additionally, some IPTV services may collect and share user data, so reviewing privacy policies is essential.
Choosing between IPTV and cable TV comes down to your priorities. If stability and reliability are your main concerns, cable TV remains a solid option. On the other hand, if you’re looking for flexibility, customization, and access to a wider range of content, IPTV is the way forward.
Jaze ISP Manager seamlessly integrates with all major IPTV, OTT platforms, and OTT aggregators, offering a fully automated solution for managing video services. Combined with Jaze’s powerful support for high-concurrency RADIUS and DIAMETER services, ISPs can efficiently manage both bandwidth and entertainment needs for triple play service, ensuring a seamless end-user experience. Click here to learn more.
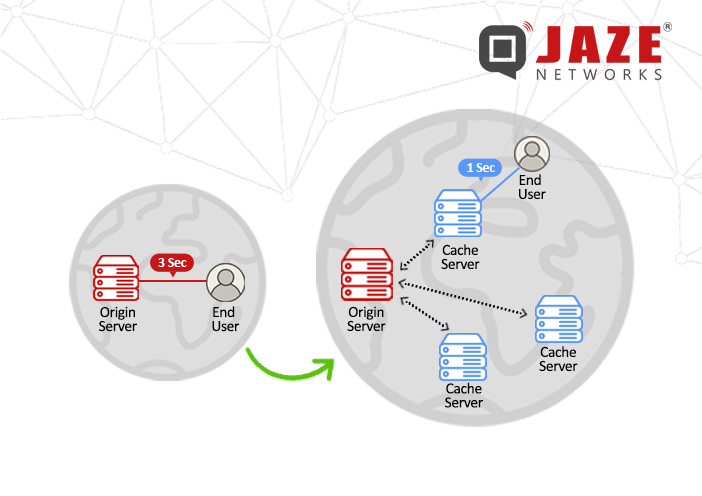
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed group of servers spread across various geographic locations, working together to efficiently deliver Internet content. The primary role of a CDN is to enhance the speed, availability, and security of websites by serving content closer to the user.
CDNs are widely used to transfer web assets like HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos. The growing reliance on CDN services means that a significant portion of today’s web traffic, including content from major platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and Facebook, is delivered via CDNs.
The key to a CDN’s functionality lies in its geographically distributed network of servers. Here’s a simplified overview of how a CDN works:
By distributing content in this way, CDNs are able to significantly enhance the performance and reliability of websites.
The advantages of using a CDN can vary depending on the size and needs of the website or application. However, the four primary benefits of a CDN are:
One of the biggest expenses for websites is the cost of bandwidth consumption for hosting. CDNs help reduce these costs by caching content, thereby reducing the load on the origin server. Since the CDN handles a significant portion of traffic, website owners can save on bandwidth expenses, making their operations more cost-efficient.
Websites often face the challenge of handling sudden spikes in traffic or dealing with hardware failures. A CDN, with its distributed infrastructure, can easily manage large volumes of traffic and better withstand hardware failures. This ensures that the website remains accessible even under heavy load, improving uptime and reliability.
Speed is a crucial factor for user experience. By serving content from servers that are closer to the end user, CDNs significantly reduce latency and enhance page load times. Faster loading websites are less likely to lose visitors due to slow performance, leading to reduced bounce rates and increased engagement. Studies show that users are more likely to leave a website if it takes too long to load, so CDNs play a vital role in improving visitor retention and satisfaction.
CDNs offer a range of security features, such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation, improved SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates, and other security optimizations. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, a CDN can help protect a website from DDoS attacks, where a server is overwhelmed by a flood of traffic. Additionally, by keeping malicious traffic away from the origin server, a CDN reduces the risk of cyberattacks and ensures that sensitive data is better protected.
CDNs play a vital role in the modern internet ecosystem by ensuring that web content is delivered quickly, reliably, and securely. Whether you’re running a small blog or a large e-commerce site, leveraging a CDN can provide significant benefits in terms of performance, cost savings, and security.
Most of the large CDN networks are available through peering at IXs. This helps ISPs who peer with them to significantly reduce bandwidth costs and deliver content faster. Jaze ISP Manager integrates with all leading BNGs which support multiple QoS policies to prioritize CDN traffic over other traffic streams. Click here to learn more
Imagine returning home after a long workday to find everything prepared for you—a cup of tea and dinner ready just as you like it. While this may seem fantastical, futurologist Ray Hammond predicts such scenarios could become reality by 2040.
The Emergence of Smart Homes
In the coming two decades, technological advancements have the potential to transform our living environments into self-sustaining ecosystems. Consider the prospect of homes constructed using 3D printing technology, with robotic workers assembling the components. This innovation could result in a substantial reduction in construction costs—potentially by as much as 60%—and timelines, allowing for new residences to be move-in ready in as little as two weeks. Equipped with smart sensors, these homes will intuitively respond to the needs of their occupants, fundamentally altering our interactions with our living spaces.
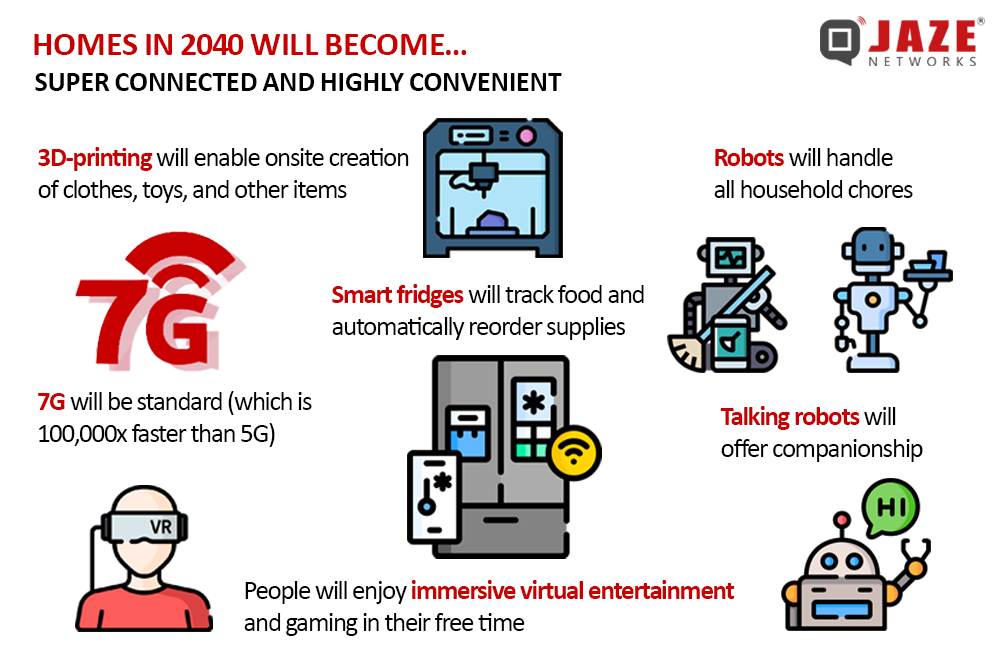
The Advent of 7G Connectivity
By 2040, the introduction of 7G technology may provide internet speeds up to 100,000 times faster than current 5G networks. Such advancements would enable the creation of immersive virtual reality experiences that blur the lines between digital and physical realities, transforming the ways we socialize, learn, and entertain ourselves.
Security in a Digital Fortress
The inconvenience of misplaced keys may become a relic of the past, as homes of the future will be secured through sophisticated facial recognition systems capable of identifying not only humans but also pets. Homeowners will have the capability to monitor their residences remotely, ensuring security even in their absence. Furthermore, continuous updates from maintenance sensors will detect potential hazards before they escalate, thereby enhancing the safety of these digitally fortified environments.
Achieving Energy Independence
Future residences are anticipated to utilize 75% less energy and to implement efficient water recycling practices. Innovations in solar technology will replace traditional bulky panels with aesthetically pleasing windows that also produce power. This move toward energy independence is vital as we strive for sustainable living solutions.
An Interactive Experience
The homes of the future will serve as responsive environments, equipped with voice recognition technology to facilitate commands for temperature adjustments, meal preparation, and more. Robotic assistants will manage household tasks, oversee grocery orders, and maintain gardens. Cooking will become increasingly effortless, as smart appliances prepare meals according to pre-programmed recipes.
Evolving Shopping and Entertainment
The potential of 3D printing may extend beyond housing to encompass clothing and household items, thus streamlining the shopping experience. Additionally, entertainment will evolve to be more interactive, integrating virtual and augmented reality. This may allow individuals to engage with holographic representations of historical figures or partake in immersive experiences that stimulate all five senses.
While the vision of future homes is intriguing, it prompts critical questions regarding the pace at which we can transition to this digital future. Factors such as technological innovation, economic conditions, and societal acceptance will play significant roles in shaping our living environments.
In the future, more devices will be connected to the Internet than ever before. Each device will require a unique IPv6 address, as the IPv4 pool is nearly exhausted. Service providers will need to roll out services exclusively on IPv6 to accommodate the increased number of connected devices. Adopting IPv6 today will ensure a smooth transition to handle the growing number of IoT devices in the future.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs deploy IPv6 services on their networks, integrating with leading BNG providers to be future-ready for IoT. By eliminating the traditional NAT with IPv4, it ensures seamless Internet connectivity. Click here to learn more.
As digital consumption continues to rise, bandwidth management has become crucial for businesses, especially those reliant on cloud services. Bandwidth, the amount of data transferred over a network in a given time, plays a significant role in determining operational costs. Without effective control, bandwidth expenses can escalate quickly, particularly in industries dependent on high volumes of data transfer.
This article will explore the key factors influencing bandwidth costs and provide strategies to reduce them.
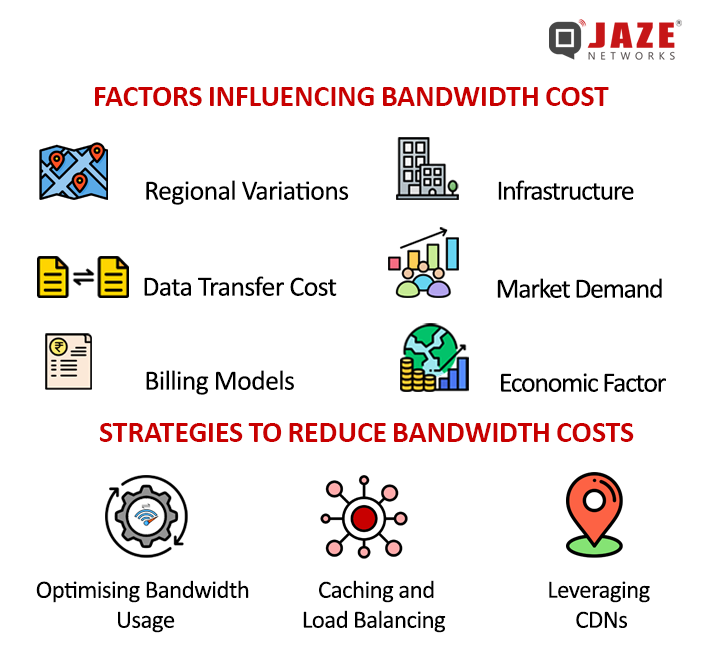
Factors Influencing Bandwidth Costs
Understanding what drives bandwidth expenses helps businesses manage their usage efficiently and avoid unnecessary costs. Here are some critical factors that affect bandwidth pricing:
1. Regional Variations
Bandwidth costs can differ based on geographic regions. Areas with advanced infrastructure and competitive markets tend to have lower costs. Conversely, regions with underdeveloped infrastructure or monopolistic market conditions face higher prices.
2. Data Transfer Costs
Many providers charge based on the volume of data transferred, typically measured in gigabytes (GB). Outbound data (sent from your network) often incurs higher costs compared to inbound data (received by your network). Providers like Google Cloud or AWS follow this model, where inbound transfers may be free, but outbound data can significantly drive up costs.
3. Billing Models
Different billing models can influence how much you pay for bandwidth:
Flat-Rate Pricing: A fixed monthly fee ensures cost predictability but may result in paying for unused bandwidth.
Pay-As-You-Go: Costs are based on actual usage, which is flexible but can lead to high expenses during peak periods.
Tiered Pricing: A tier-based approach offers a balance of predictability and flexibility, accommodating business growth.
4. Infrastructure and Peering
Regions with well-developed peering exchanges enable more efficient data transfer between networks. This reduces bandwidth costs by lowering the need for long-distance data transmission.
5. Economic Factors
Bandwidth costs are also affected by external factors such as power, cooling, and real estate costs. Data centers located in regions with high electricity prices or expensive real estate tend to pass those costs onto their customers.
6. Market Demand
In areas of high internet demand, especially during peak times, service providers may increase prices. High market demand for bandwidth can drive up prices, particularly in growing internet markets.
Strategies to Reduce Bandwidth Costs
To manage bandwidth expenses effectively, businesses must adopt strategies that optimize their data usage. Here are some key ways to reduce bandwidth costs:
1. Optimizing Bandwidth Usage
Managing bandwidth usage is essential for minimizing unnecessary data transfer:
Data Management: Prioritize essential data transfers and schedule non-essential ones during off-peak hours to reduce congestion.
Compression Techniques: Compressing large files such as images or videos before transferring them can drastically reduce the amount of data sent, lowering bandwidth costs.
Monitor Usage: Regularly analyzing bandwidth usage can reveal inefficiencies or heavy usage patterns, guiding businesses to implement specific cost-saving measures.
2. Caching and Load Balancing
Caching allows frequently accessed data to be stored locally, reducing repeated data transfers. For instance, implementing caching for images or videos can drastically cut data transfer to and from the server. Load balancing helps distribute network traffic across multiple servers, reducing the strain on any single server and preventing bandwidth overuse.
3. Using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN consists of a network of servers distributed across multiple locations, which cache and deliver content closer to users. CDNs reduce the load on the original server by handling static content like images, CSS files, and videos. This minimizes the need for repeated data transfer from the origin server, leading to significant bandwidth savings. CDNs are highly effective, often managing 60-80% of a website’s bandwidth, allowing the original server to focus on more critical functions.
Monitoring bandwidth usage regularly will also help businesses avoid unexpected costs and ensure more efficient network management. Implementing these methods can provide both immediate savings and long-term benefits, making them crucial for growing companies in today’s digital landscape.
Jaze ISP Manager provides comprehensive tools for monitoring bandwidth usage, offering real-time insights and detailed usage reports. This solution enables Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to manage end-to-end operations, including subscriber lifecycle management, billing, and policy enforcement. With features like automated provisioning, flexible billing options, and integration with various network equipment, Jaze ISP Manager helps businesses optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient network performance. Click here to learn more